| Control System Toolbox Function Reference |   |
Functions by Category
| Function Name |
Description |
|
Generate random discrete state-space model |
|
Create descriptor state-space model |
|
Create discrete filter with DSP convention |
|
Create a frequency response data (FRD) model |
|
Retrieve data from an FRD model |
|
Query LTI model properties |
|
Generate random continuous state-space model |
|
Set LTI model properties |
|
Create state-space model |
|
Retrieve state-space data |
|
Create transfer function |
|
Retrieve transfer function data |
|
Provide the aggregate delay for an LTI model |
|
Create zero-pole-gain model |
|
Retrieve zero-pole-gain data |
| Function Name |
Description |
|
Display model type ('tf', 'zpk', 'ss', or 'frd') |
|
Test true if LTI model has any type of delay |
|
Test true if LTI model is of specified type |
|
Test true for continuous-time models |
|
Test true for discrete-time models |
|
Test true for empty LTI models |
|
Test true for proper LTI models |
|
Test true for SISO models |
|
Display the number of model/array dimensions |
|
Display output/input/array dimensions |
| Function Name |
Description |
|
Convert from continuous- to discrete-time models |
|
Convert the units property for FRD models |
|
Convert from discrete- to continuous-time models |
|
Resample discrete-time models |
|
Convert delays in discrete-time models or FRD models |
|
Convert to a frequency response data model |
|
Compute the Padé approximation of delays |
|
Change the shape of an LTI array |
|
Provide partial fraction expansion |
|
Convert to a state space model |
|
Convert to a transfer function model |
|
Convert to a zero-pole-gain model |
| Function Name |
Description |
|
Calculate an I/O balanced realization |
|
Calculate minimal realization or eliminate pole/zero pairs |
|
Delete states in I/O balanced realization |
|
Calculate structured model reduction |
| Function Name |
Description |
|
Canonical state-space realizations |
|
Controllability matrix |
|
Controllability staircase form |
|
Controllability and observability grammians |
|
Observability matrix |
|
Observability staircase form |
|
State coordinate transformation. |
|
Diagonal balancing of state-space realizations. |
| Function Name |
Description |
|
Calculate natural frequency and damping |
|
Calculate low-frequency (DC) gain |
|
Calculate covariance of response to white noise |
|
Sort discrete-time poles by magnitude |
|
Sort continuous-time poles by real part |
|
Calculate norms of LTI models (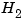 and and 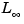 ) ) |
|
Calculate the poles of an LTI model |
|
Plot the pole/zero map of an LTI model |
|
Calculate and plot root locus |
|
Calculate roots of polynomial |
|
Superimpose s- and z-plane grids for root locus or pole/zero maps |
|
Calculate zeros of an LTI model |
| Function Name |
Description |
|
Append models in a block diagonal configuration |
|
Augment output by appending states |
|
Connect the subsystems of a block-diagonal model according to an interconnection scheme of your choice |
|
Calculate the feedback connection of models |
|
Form the LFT interconnection (star product) |
|
Generate second-order model |
|
Create a generalized parallel connection |
|
Create a generalized series connection |
|
Stack LTI models into a model array |
| Function Name |
Description |
|
Generate an input signal |
|
Calculate and plot impulse response |
|
Calculate and plot initial condition response |
|
Simulate response of LTI model to arbitrary inputs |
|
Open the LTI Viewer for linear response analysis |
|
Calculate step response |
| Function Name |
Description |
|
Convert delays in discrete-time models or FRD models |
|
Compute the Padé approximation of delays |
|
Provide the aggregate delay for an LTI model |
| Function Name |
Description |
|
Calculate all crossover frequencies and associated gain, phase, and delay margins |
|
Calculate and plot Bode response |
|
Calculate and plot Bode magnitude only |
|
Evaluate response at single complex frequency |
|
Evaluate frequency response for selected frequencies |
|
Interpolate FRD model between frequency points |
|
Create a vector of evenly spaced frequencies |
|
Create a vector of logarithmically spaced frequencies |
|
Open the LTI Viewer for linear response analysis |
|
Calculate gain and phase margins |
|
Superimpose grid lines on a Nichols plot |
|
Calculate Nichols plot |
|
Calculate Nyquist plot |
|
Calculate singular value plot |
| Function Name |
Description |
allmargin |
Calculate all crossover frequencies and associated gain, phase, and delay margins |
margin |
Calculate gain and phase margins |
rlocus |
Calculate and plot root locus |
sisotool |
Open the SISO Design Tool |
| Function Name |
Description |
|
Calculate SISO pole placement design |
|
Calculate MIMO pole placement design |
|
Form state estimator given estimator gain |
|
Form output-feedback compensator given state-feedback and estimator gains |
| Function Name |
Description |
|
Calculate the LQ-optimal gain for continuous models |
|
Calculate the LQ-optimal gain for discrete models |
|
Calculate the LQ-optimal gain with output weighting |
|
Calculate the discrete LQ gain for continuous models |
|
Calculate the Kalman estimator |
|
Calculate the discrete Kalman estimator for continuous models |
|
Form LQG regulator given LQ gain and Kalman filter |
| Function Name |
Description |
|
Solve continuous-time algebraic Riccati equations |
|
Solve discrete-time algebraic Riccati equations |
|
Solve continuous-time Lyapunov equations |
|
Solve discrete-time Lyapunov equations |
| Function Name |
Description |
|
Open the LTI Viewer for linear response analysis |
|
Open the SISO Design GUI |
 | Function Reference | Alphabetical List of Functions |  |