| Control System Toolbox Function Reference |   |
Form regulator given state-feedback and estimator gains
Syntax
rsys = reg(sys,K,L) rsys = reg(sys,K,L,sensors,known,controls)
Description
rsys = reg(sys,K,L)
forms a dynamic regulator or compensator rsys given a state-space model sys of the plant, a state-feedback gain matrix K, and an estimator gain matrix L. The gains K and L are typically designed using pole placement or LQG techniques. The function reg handles both continuous- and discrete-time cases.
This syntax assumes that all inputs of sys are controls, and all outputs are measured. The regulator rsys is obtained by connecting the state-feedback law 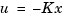 and the state estimator with gain matrix
and the state estimator with gain matrix L (see estim). For a plant with equations
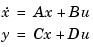
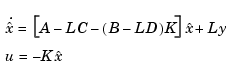
This regulator should be connected to the plant using positive feedback.
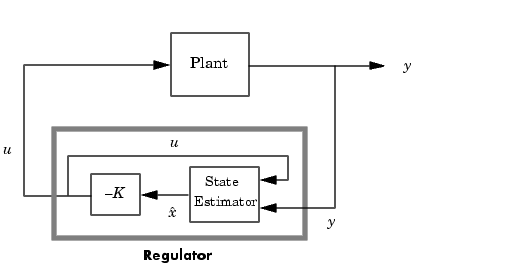
rsys = reg(sys,K,L,sensors,known,controls)
handles more general regulation problems where:
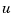 , known inputs
, known inputs 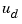 , and stochastic inputs
, and stochastic inputs 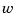 .
.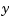 of the plant outputs is measured.
of the plant outputs is measured.The index vectors sensors, known, and controls specify 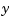 ,
, 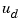 , and
, and 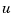 as subsets of the outputs and inputs of
as subsets of the outputs and inputs of sys. The resulting regulator uses 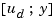 as inputs to generate the commands
as inputs to generate the commands 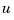 (see figure below).
(see figure below).
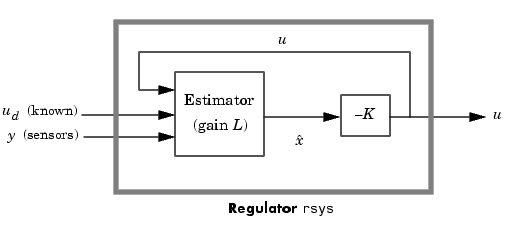
Example
Given a continuous-time state-space model
sys = ss(A,B,C,D)
with seven outputs and four inputs, suppose you have designed:
K using inputs 1, 2, and 4 of the plant as control inputsL using outputs 4, 7, and 1 of the plant as sensors, and input 3 of the plant as an additional known inputYou can then connect the controller and estimator and form the complete regulation system by
controls = [1,2,4]; sensors = [4,7,1]; known = [3]; regulator = reg(sys,K,L,sensors,known,controls)
See Also
estim
kalman
lqgreg
lqr, dlqr
place
 | pzmap | reshape |  |