| Release 11 New Features |
DSP Blockset 3.0
Version 3.0 of the DSP Blockset is a major release, and introduces a substantial set of new features:Dedicated complex blocks (such as Complex To Workspace and Mag/Angle Join) have been removed from the blockset.
Some of these complex blocks have been merged with their real counterparts. For example, the Version 2.2 FFT and Complex FFT blocks are now a single block, FFT. Other complex-data blocks, including most of those in the 2.2 Complex library, are now a part of the Simulink library (usually under different names). Examples are the 2.2 Real and Imag blocks, which are now combined as the Complex to Real-Imag block.
Most blocks that operate on sequential time-samples now offer a Frame-based inputs checkbox in the parameter dialog box. When you check the box, the block accepts frames of buffered time-samples rather than a scalar sequence over time. Frame-based processing can return great increases in efficiency for both simulated and compiled models.
The Sample time field in the parameter dialog box has been removed from almost all blocks. Blocks now automatically detect the sample times of inputs. Source blocks (such as Signal From Workspace) still retain the Sample time parameter.
readme file for a summary of the new additions. To view the readme file, at the MATLAB command line type
info dspblksNote
Running Different Blockset Versions
When you install the DSP Blockset 3.0 on your computer, Version 2.2 of the blockset is also installed. Run Version 3.0 by typingdsplib. To run Version 2.2, type dsplib 2.
Incompatibilities Between 3.0 and 2.2
Because of the extensive changes introduced in this release to support the new Simulink complex data format, incompatibilities can arise when 3.0 blocks are used in models containing 2.2 blocks. See "Upgrading to DSP Blockset 3.0 and Communications Toolbox 1.4" in Chapter 4 for information about migrating a model to the current version.Library Structure
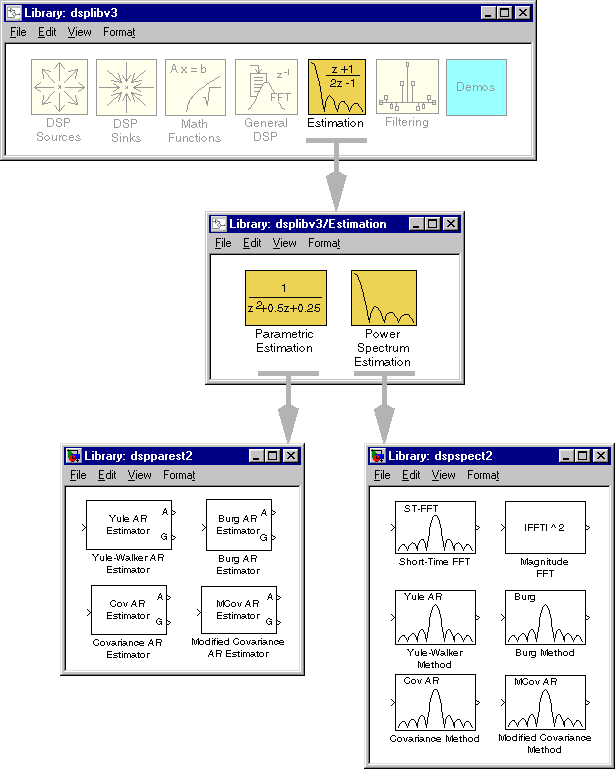
The library structure has undergone further refinement for Version 3.0. The major alterations are:

Data Frames
Most blocks whose operation can benefit from block processing now accept data frames, vectors whose elements represent consecutive time samples from a single signal. Framed data is a common format in real-time systems, where the data acquisition hardware often operates most efficiently by accumulating a large number of signal samples at a high rate, and then propagating these samples to the real-time system as a block, or frame, of data. Data frames can also be constructed through the usual DSP Blockset buffering operations (using the Buffer block, for example). See "Working with Samples and Frames" in Chapter 2 of the User's Guide for a complete discussion of the frame data format, and how to use it to improve model efficiency.Upgrading Your Models to Use Data Frames
You can realize large improvements in the efficiency of your models by using data frames whenever possible. Although throughput gains are particularly pronounced in systems where the sampled data is introduced in a framed format (such as speech and audio), non-real-time simulations also benefit as a result of the reduction in block-to-block communication overhead.Complex Data
All blocks in the DSP Blockset are now capable of processing both real and complex data (using Simulink's new complex data type). In cases where two separate blocks were previously provided for real and complex inputs (e.g., FFT and Complex FFT), there is now a single block (FFT) that operates on both real and complex data. This enhancement greatly simplifies the contents of most libraries, in addition to allowing the removal of the Complex library from Math Functions. Blocks in the Complex library that could not be combined with a real data counterpart (e.g., Imag) are now in the Simulink Math library (usually under a different name). Table 1-2 lists the new names and locations of all former 2.2 blocks. If any of your models use complex data, be sure to read "Why You Need to Update Your Models to Use the New Complex Data Format" in Chapter 4 before adding any Version 3.0 blocks.Multirate Sample Time Enhancements
As a result of the multirate sample time enhancements in Simulink 3.0, all nonsource DSP blocks now inherit and propagate their sample times. This means that you do not need to track sample times manually throughout a model; when you make a change to the sample time of a source block, all other DSP blocks in the model automatically adjust to the propagated sample time.New and Enhanced Blocks
Table 1-1 lists the new blocks in Version 3.0. Among the most significant additions are the linear algebra blocks and real-time audio blocks.| Block Library |
Block Name |
Purpose |
| DSP Sources | Chirp |
Generate a swept-frequency cosine. |
| Discrete Constant |
Generate a constant. |
|
| From Wave Device |
Read audio data from a standard audio device in real-time (Windows 95/98/NT only). |
|
| From Wave File |
Read audio data from a Microsoft Wave (.wav) file (Windows 95/98/NT only). |
|
| Triggered Signal From Workspace |
Acquire and output a workspace signal when triggered. |
|
| Sine Wave |
Generate one or more sine waves. |
|
| DSP Sinks | Buffered FFT Frame Scope |
Compute and display the frequency content of an input sequence. |
| FFT Frame Scope |
Compute and display the frequency content of a framed input. |
|
| Frequency Frame Scope |
Display frame-based data. |
|
| Matrix Viewer |
Display a matrix as an image with values mapped to colors. |
|
| Time Frame Scope |
Display frame-based data. |
|
| To Wave Device |
Send audio data to a standard audio device in real-time (Windows 95/98/NT only). |
|
| To Wave File |
Write audio data to file in the Microsoft Wave (.wav) format (Windows 95/98/NT only). |
|
| User-defined Frame Scope |
Display frame-based data. |
|
| Elementary Functions | Contiguous Copy |
Recreate the input in a contiguous block of memory (for code generation). |
| Convert Complex DSP to Simulink |
Convert complex data from the DSP Blockset v2.2 format to the Simulink v3 format. |
|
| Convert Complex Simulink to DSP |
Convert complex data from the Simulink v3 format to the DSP Blockset v2.2 format. |
|
| Inherit Complexity |
Change the complexity of the input to match that of a reference signal. |
|
| Variable Selector |
Select a subset of elements (submatrix) in a matrix. |
|
| Matrix Functions | Create Diagonal Matrix |
Create a matrix from a vector diagonal. |
| Extract Diagonal |
Create a vector from the elements of a matrix diagonal. |
|
| Extract Triangular Matrix |
Extract the lower or upper triangle from an input matrix. |
|
| Matrix Product |
Multiply the elements on a specified matrix row or column. |
|
| Matrix Scaling |
Scale the rows or columns of a matrix by a specified vector. |
|
| Matrix Sum |
Sum the elements on a specified matrix row or column. |
|
| Permute Matrix |
Reorder the rows or columns of a matrix. |
|
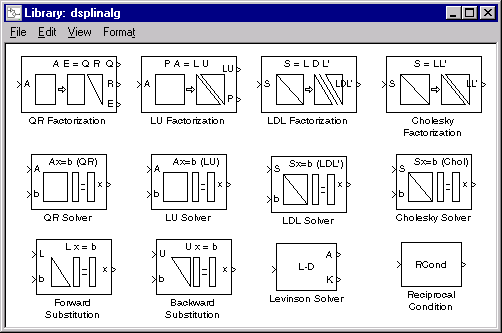
| Linear Algebra | Backward Substitution |
Solve the equation Ux=b for upper triangular matrix U. |
| Cholesky Factorization |
Factor a Hermitian positive definite matrix into triangular components. |
|
| Cholesky Solver |
Solve the equation Sx=b for Hermitian positive definite matrix S. |
|
| Forward Substitution |
Solve the equation Lx=b for lower triangular matrix U. |
|
| LDL Factorization |
Factor a Hermitian positive definite matrix into lower, upper, and diagonal components. |
|
| LDL Solver |
Solve the equation Sx=b for Hermitian positive definite matrix S. |
|
| LU Factorization |
Factor a square matrix into lower and upper triangular components. |
|
| LU Solver |
Solve the equation Ax=b for square matrix A. |
|
| QR Factorization |
Factor a rectangular matrix into unitary and upper triangular components. |
|
| QR Solver |
Find a minimum-norm-residual solution to the equation Ax=b. |
|
| Reciprocal Condition |
Compute the reciprocal condition of a square matrix in the 1-norm. |
|
| Buffers | Queue |
Buffer inputs into a FIFO (first input, first output) register. |
| Rebuffer |
Increase or decrease the size of the input frame. |
|
| Stack |
Buffer inputs into a LIFO (last input, first output) register. |
|
| Switches and Counters | Counter |
Count up or down through a specified range of numbers. |
| Edge Detector |
Detect transition of input from zero to non-zero value. |
|
| Event-Count Comparator |
Detect threshold crossing of accumulated non-zero events. |
|
| Multiphase Clock |
Generate multiple binary clock signals. |
|
| Parametric Estimation | Burg AR Estimator |
Compute an estimate of AR model parameters using the Burg method. |
| Covariance AR Estimator |
Compute an estimate of AR model parameters using the covariance method. |
|
| Modified Covariance AR Estimator |
Compute an estimate of AR model parameters using the modified covariance method. |
|
| Yule-Walker AR Estimator |
Compute an estimate of AR model parameters using the Yule-Walker method. |
|
| Power Spectrum Estimation | Covariance Method |
Compute a parametric spectral estimate using the covariance method. |
| Magnitude FFT |
Compute a nonparametric estimate of the spectrum using the periodogram method. |
|
| Modified Covariance Method |
Compute a parametric spectral estimate using the modified covariance method. |
|
| Short-Time FFT |
Compute a nonparametric estimate of the spectrum using the modified, averaged periodogram method. |
|
| Filter Realizations | Biquadratic Filter |
Apply a cascade of biquadratic (second-order-section) filters to the input. |
| Direct-Form II Transpose Filter |
Apply an IIR filter to the input. |
|
| Time-Varying Direct-Form II Transpose Filter |
Apply a variable IIR filter to the input. |
|
| Time-Varying Lattice Filter |
Apply a variable lattice filter to the input. |
|
| Multirate Filters | Dyadic Analysis Filter Bank |
Decompose a signal using a dyadic multirate filter bank. |
| Dyadic Synthesis Filter Bank |
Reconstruct a signal using a dyadic multirate filter bank. |
| 2.2 Block Name |
3.0 Block Name |
Library Location |
| Analog Filter Design |
same |
same |
| Analytic Signal |
same |
same |
| Angle |
Complex to Magnitude-Angle |
Simulink |
| Autocorrelation |
same |
same |
| Buffer |
same |
same |
| Buffered FFT Scope |
Buffered FFT Frame Scope |
same |
| Burg Method |
same |
Power Spectrum Estimation |
| Commutator |
same |
same |
| Complex Autocorrelation |
Autocorrelation |
same |
| Complex Buffer |
Buffer |
same |
| Complex Buffered FFT Scope |
Buffered FFT Frame Scope |
same |
| Complex Cepstrum |
same |
same |
| Complex Constant |
Constant |
Simulink |
| Complex Delay |
Integer Delay |
same |
| Complex Demux |
Demux |
Simulink |
| Complex Diagonal Matrix |
Constant Diagonal Matrix |
same |
| Complex Dot Product |
Dot Product |
Simulink |
| Complex Exponential |
same |
Elementary Functions |
| Complex FFT Scope |
FFT Frame Scope |
same |
| Complex Flip |
Flip |
same |
| Complex From Workspace |
Signal From Workspace |
same |
| Complex Gain |
Gain |
Simulink |
| Complex Kalman Adaptive Filter |
Kalman Adaptive Filter |
same |
| Complex Levinson-Durbin |
Levinson Solver |
same |
| Complex LMS Adaptive Filter |
LMS Adaptive Filter |
same |
| Complex LPC |
LPC |
same |
| Complex Matrix Constant |
Matrix Constant |
same |
| Complex Matrix From Workspace |
Matrix From Workspace |
same |
| Complex Matrix Multiplication |
Matrix Multiplication |
same |
| Complex Matrix To Workspace |
Matrix To Workspace |
same |
| Complex Multiply |
Product |
Simulink |
| Complex Mux |
Mux |
Simulink |
| Complex Normalization |
Normalization |
same |
| Complex Partial Unbuffer |
Partial Unbuffer |
same |
| Complex Reciprocal |
Math Function |
Simulink |
| Complex RLS Adaptive Filter |
RLS Adaptive Filter |
same |
| Complex Selector |
Selector |
Simulink |
| Complex Submatrix |
Submatrix |
same |
| Complex Sum |
Sum |
Simulink |
| Complex To Workspace |
To Workspace |
Simulink |
| Complex Transpose |
Transpose |
same |
| Complex Unbuffer |
Unbuffer |
same |
| Complex Unit Delay |
Integer Delay |
same |
| Complex Width |
Width |
Simulink |
| Complex Zero Pad |
Zero Pad |
same |
| Conjugate |
Math Function |
Simulink |
| Constant Exponent |
Math Function |
Simulink |
| Convolution |
same |
same |
| Convolution C-C |
Convolution |
same |
| Convolution C-R |
Convolution |
same |
| Correlation |
same |
same |
| Correlation C-C |
Correlation |
same |
| Correlation C-R |
Correlation |
same |
| Cumulative Sum |
same |
same |
| dB |
same |
Elementary Functions |
| dB Gain |
same |
Elementary Functions |
| DCT |
same |
same |
| Delay |
Integer Delay |
same |
| Detrend |
same |
same |
| Diagonal Matrix |
Constant Diagonal Matrix |
same |
| Difference |
same |
same |
| Digital FIR Filter Design |
same |
same |
| Digital IIR Filter Design |
same |
same |
| Distributor |
same |
same |
| Dot Product |
same |
Simulink |
| Downsample |
same |
same |
| FFT |
same |
same |
| FFT Scope |
FFT Frame Scope |
same |
| Filter |
Discrete Filter |
Simulink |
| Filter Realization Wizard |
same |
same |
| FIR Decimation |
same |
same |
| FIR Interpolation |
same |
same |
| FIR Rate Conversion |
same |
same |
| FIR Rate Conversion (Frame) |
FIR Rate Conversion |
same |
| Fixed Truncation |
Rounding Function |
Simulink |
| Flip |
same |
same |
| Frequency Vector Scope |
Frequency Frame Scope |
same |
| Hermitian Transpose |
Transpose |
same |
| Histogram |
same |
same |
| IDCT |
same |
same |
| IFFT |
same |
same |
| Imag |
Complex to Real-Imag |
Simulink |
| Inverse-FFT FIR Filter Design |
obsolete |
same |
| Join |
Real-Imag to Complex |
Simulink |
| Kalman Adaptive Filter |
same |
same |
| Least Squares FIR Filter Design |
same |
same |
| Levinson-Durbin |
Levinson Solver |
Linear Algebra |
| LMS Adaptive Filter |
same |
same |
| LPC |
same |
same |
| Mag/Angle Join |
Magnitude-Angle to Complex |
Simulink |
| Mag/Angle Split |
Complex to Magnitude-Angle |
Simulink |
| Magnitude |
Abs |
Simulink |
| Magnitude Squared |
Math Function |
Simulink |
| Math Function |
same |
Simulink |
| Matrix Constant |
same |
same |
| Matrix From Workspace |
same |
same |
| Matrix Multiplication |
same |
same |
| Matrix To Workspace |
same |
same |
| Maximum |
same |
same |
| Mean |
same |
same |
| Median |
same |
same |
| Minimum |
same |
same |
| Multichannel IIR Filter |
Direct-Form II Transpose Filter |
same |
| Multichannel IIR Filter (Frame) |
Direct-Form II Transpose Filter |
same |
| N-Sample Enable |
same |
same |
| N-Sample Enable w/Reset |
N-Sample Enable |
same |
| N-Sample Switch |
same |
same |
| Normalization |
same |
same |
| Overlap-Add FFT Filter |
same |
same |
| Overlap-Save FFT Filter |
same |
same |
| Partial Unbuffer |
same |
same |
| Periodogram |
Short-Time FFT |
Power Spectrum Estimation |
| Quantizer |
same |
Simulink |
| Real |
Complex to Real-Imag |
Simulink |
| Real Cepstrum |
same |
same |
| Real DCT |
DCT |
same |
| Real FFT |
FFT |
same |
| Real IDCT |
IDCT |
same |
| Real IFFT |
IFFT |
same |
| Real To Complex |
Real-Imag to Complex |
Simulink |
| Remez FIR Filter Design |
same |
same |
| Repeat |
same |
same |
| Reshape |
same |
same |
| RLS Adaptive Filter |
same |
same |
| RMS |
same |
same |
| Rounding Function |
same |
Simulink |
| Running Histogram |
Histogram |
same |
| Running Maximum |
Maximum |
same |
| Running Mean |
Mean |
same |
| Running Minimum |
Minimum |
same |
| Running RMS |
RMS |
same |
| Running Standard Deviation |
Standard Deviation |
same |
| Running Variance |
Variance |
same |
| Sample and Hold |
same |
same |
| Shift Register |
same |
same |
| Sign |
same |
Simulink |
| Signal From Workspace |
same |
same |
| Sort |
same |
same |
| Split |
Complex to Real-Imag |
Simulink |
| Standard Deviation |
same |
same |
| Submatrix |
same |
same |
| Time Varying FIR Filter |
Time-Varying Direct-Form II Transpose Filter |
same |
| Time Varying IIR Filter |
Time-Varying Direct-Form II Transpose Filter |
same |
| Time Vector Scope |
Time Frame Scope |
same |
| To Workspace |
Signal To Workspace |
same |
| Toeplitz |
same |
same |
| Transpose |
same |
same |
| Triggered Complex Matrix To Workspace |
Triggered Matrix To Workspace |
same |
| Triggered Complex To Workspace |
Triggered Signal To Workspace |
same |
| Triggered Matrix To Workspace |
same |
same |
| Triggered Shift Register |
same |
same |
| Triggered To Workspace |
Triggered Signal To Workspace |
same |
| Trigonometric Function |
same |
Simulink |
| Unbuffer |
same |
same |
| Unit Delay |
Integer Delay |
same |
| Unwrap |
same |
same |
| Upsample |
same |
same |
| Variable Fractional Delay |
same |
same |
| Variable Integer Delay |
same |
same |
| Variance |
same |
same |
| Width |
same |
Simulink |
| Window Function |
same |
same |
| Yule-Walker AR |
Yule-Walker Method |
Power Spectrum Estimation |
| Yule-Walker IIR Filter Design |
same |
same |
| Zero Pad |
same |
same |