| DSP Blockset |   |
Compute the correlation along the columns of two inputs.
Library
Description
The Correlation block computes the cross-correlation of corresponding columns (channels) of the Mu-by-N input matrix u and Mv-by-N input matrix v. The frame status of both inputs must be the same. The block does not accept sample-based full-dimension matrix inputs or 2-D row vector inputs.
Frame-Based Inputs
Matrix inputs must be frame-based. The output, y, is a frame-based (Mu+Mv-1)-by-N matrix whose jth column has elements
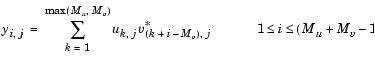
where * denotes the complex conjugate. Inputs u and v are zero when indexed outside of their valid ranges. When both inputs are real, the output is real; when one or both inputs are complex, the output is complex.
When one input is a column vector (single channel) and the other is a matrix (multiple channels), the single-channel input is independently cross-correlated with each channel of the multichannel input. For example, if u is a Mu-by-1 column vector and v is an Mv-by-N matrix, the output is an (Mu+Mv-1)-by-N matrix whose jth column has elements
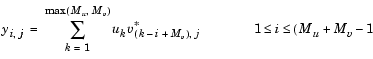
Sample-Based Inputs
Matrix inputs cannot be sample based, so all sample-based inputs are column vectors or 1-D vectors. (the block does not support 2-D row vector inputs.) If u and v are sample-based vectors with lengths Mu and Mv, the Correlation block performs the vector cross-correlation
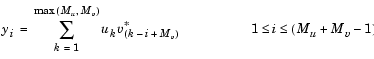
The dimensions of the sample-based output vector are determined by the dimensions of the input vectors:
The Correlation block does not accept sample-based full-dimension matrix inputs or 2-D row vector inputs.
Dialog Box
See Also
| Autocorrelation |
DSP Blockset |
| Convolution |
DSP Blockset |
xcorr |
Signal Processing Toolbox |
 | Convolution | Counter |  |