| Using Simulink |   |
Combine several input signals into a vector or bus output signal.
Library
Description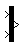
The Mux block combines its inputs into a single output. An input can be a scalar, vector, or matrix signal. Depending on its inputs, the output of a Mux block is a vector or a composite signal, i.e., a signal containing both matrix and vector elements. If all of a Mux block's inputs are vectors or vector-like, the block's output is a vector. A vector-like signal is any signal that is a scalar (one-element vector), a vector, or a single-column or single-row matrix. If any input is a nonvector-like matrix signal, the output of the Mux is a bus signal. Bus signals can drive only virtual blocks, e.g., a Demux, Subsystem, or Go To block.
The Mux block's Number of Inputs parameter allows you to specify input signal names and dimensionality as well as the number of inputs. You can use any of the following formats to specify this parameter:
Specifies the number of inputs to the Mux block. When this format is used, the block accepts signals of any dimensionality. Also, Simulink assigns each input the name signalN, where N is the input port number.
The length of the vector specifies the number of inputs. Each element specifies the dimensionality of the corresponding input. A positive value specifies that the corrresponding port can accept only vectors of that size. For example [2 3] specifies two input ports of size 2 and 3, respectively. If an input signal width does not match the expected width, Simulink displays an error message. A value of -1 specifies that the corresponding port can accept vectors or matrices of any dimensionality.
The length of the cell array specifies the number of inputs. The value of each cell specifies the dimensionality of the corresponding input. A scalar value N specifies a vector of size N. A vector value [M N] specifies an MxN matrix. A value of -1 means the corresponding port can accept signals of any dimensionality.
You can enter a list of signal names separated by commas. Simulink assigns each name to the corresponding port and signal. For example, if you enter position,velocity, the Mux block will have two inputs, named position and velocity.
| Note Simulink hides the name of a Mux block when you copy it from the Simulink block library to a model. |
Data Type Support
A Mux block accepts real or complex signals of any data type, including mixed-type vectors.
Parameters and Dialog Box
| Display Option |
Appearance of Block in Model |
none |
Mux appears inside block icon |
signals |
Displays signal names next to each port |
bar |
Displays the block icon in a solid foreground color |
 | Multiport Switch | Outport |  |