| DSP Blockset |   |
Compute a window, and/or apply a window to an input signal.
Library
DSP Sources, Signal Operations
Description
The Window Function block has three modes of operation, selected by the Operation parameter as described below.
Operation Modes
In each mode, the block first creates a window vector, w, by sampling the window specified in the Window type parameter at M discrete points. The Operation modes are:
In this mode the block computes an M-by-1 window vector, w, and multiplies the vector element-wise with each of the N channels in the M-by-N input matrix u.
y = repmat(w,1,N) .* u % Equivalent MATLAB code
A length-M 1-D vector input is treated as an M-by-1 matrix. The output, y, always has the same dimension as the input. If the input is frame-based, the output is frame-based; otherwise, the output is sample-based.
In this mode the block generates a sample-based 1-D window vector, w, with length M specified by the Window length parameter. The In port is disabled.
In this mode the block computes an M-by-1 window vector, w, and multiplies the vector element-wise with each of the N channels in the M-by-N input matrix u.
y = repmat(w,1,N) .* u % Equivalent MATLAB code
A length-M 1-D vector input is treated as an M-by-1 matrix. The block produces two outputs:
Out port, the block produces the result of the multiplication, y, which has the same dimension as the input. If the input is frame-based, output y is frame-based; otherwise, output y is sample-based.Win port, the block produces the M-by-1 window vector, w. Output w is always sample-based.Window Sampling
For the generalized-cosine windows (Blackman, Hamming, and Hann), the Sampling parameter determines whether the window samples are computed in a periodic or a symmetric manner. For example, if Sampling is set to Symmetric, a Hamming window of length M is computed as
w = hamming(M) % Symmetric (aperiodic) window
If Sampling is set to Periodic, the same window is computed as
w = hamming(M+1) % Periodic (asymmetric) window w = w(1:M)
Window Type
The available window types are shown in the table below. The Stopband attenuation in dB and Beta parameters specify the characteristics of the Chebyshev and Kaiser windows, respectively, and are only available when those window designs are selected.
When Window type is set to User defined, the Window function block computes the user-defined window specified by the Window function name parameter. If the user-defined window requires parameters other than the window length, select the Additional parameters for user defined window check box. The cell array entered in Window function parameters determines the values of the additional parameters.
For complete information about the other window functions, consult the Signal Processing Toolbox documentation.
| Window Type |
Description |
| Bartlett |
w =
|
| Blackman |
w =
|
| Boxcar |
w =
|
| Chebyshev |
Computes a Chebyshev window with stopband ripple w =
|
| Hamming |
w =
|
| Hann |
Computes a Hann window (also known as a Hanning window). w =
|
| Hanning |
Obsolete. This window option is included only for compatibility with older models. Use the Hann option instead of Hanning whenever possible. |
| Kaiser |
Computes a Kaiser window with Kaiser parameter w =
|
| Triang |
w =
|
| User Defined |
Computes the user-defined window function specified by the entry in the Window function name parameter, w = |
Dialog Box
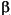 parameter. Increasing
parameter. Increasing 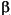 widens the mainlobe and decreases the amplitude of the window sidelobes in the window's frequency magnitude response. Tunable.
widens the mainlobe and decreases the amplitude of the window sidelobes in the window's frequency magnitude response. Tunable.See Also
| FFT |
DSP Blockset |
bartlett |
Signal Processing Toolbox |
blackman |
Signal Processing Toolbox |
boxcar |
Signal Processing Toolbox |
chebwin |
Signal Processing Toolbox |
hamming |
Signal Processing Toolbox |
hann |
Signal Processing Toolbox |
kaiser |
Signal Processing Toolbox |
triang |
Signal Processing Toolbox |
 | Wavelet Synthesis | Yule-Walker AR Estimator |  |