| Communications Toolbox |   |
Multiply elements of a Galois field
Syntax
c = gfmul(a,b); c = gfmul(a,b,p); c = gfmul(a,b,field);
Description
The gfmul function multiplies elements of a Galois field. (To multiply polynomials over a Galois field, use gfconv instead.)
c = gfmul(a,b)
multiplies a and b in GF(2). Each entry of a and b is either 0 or 1. If a and b are matrices of the same size, then the function treats each element independently.
c = gfmul(a,b,p)
multiplies a and b in GF(p). Each entry of a and b is between 0 and p-1. p is a prime number. If a and b are matrices of the same size, then the function treats each element independently.
c = gfmul(a,b,field)
multiplies a and b in GF(pm), where p is a prime number and m is a positive integer. a and b represent elements of GF(pm) in exponential format relative to some primitive element of GF(pm). field is the matrix listing all elements of GF(pm), arranged relative to the same primitive element. c is the exponential format of the product, relative to the same primitive element. See Representing Elements of Galois Fields for an explanation of these formats. If a and b are matrices of the same size, then the function treats each element independently.
Examples
The section Arithmetic in Galois Fields contains examples. Also, the code below shows that 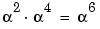 , where
, where 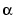 is a root of the primitive polynomial 2 + 2x + x2 for GF(9).
is a root of the primitive polynomial 2 + 2x + x2 for GF(9).
p = 3; m = 2;
primpoly = [2 2 1];
field = gftuple([-1:p^m-2]',primpoly,p);
a = gfmul(2,4,field)
a =
6
See Also
gfdiv, gfconv, gfdeconv, gftuple
 | gfminpol | gfplus |  |