| Statistics Toolbox |   |
Finding the Similarities Between Objects
You use the pdist function to calculate the distance between every pair of objects in a data set. For a data set made up of m objects, there are 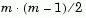 pairs in the data set. The result of this computation is commonly known as a similarity matrix (or dissimilarity matrix).
pairs in the data set. The result of this computation is commonly known as a similarity matrix (or dissimilarity matrix).
There are many ways to calculate this distance information. By default, the pdist function calculates the Euclidean distance between objects; however, you can specify one of several other options. See pdist for more information.
Note
You can optionally normalize the values in the data set before calculating the distance information. In a real world data set, variables can be measured against different scales. For example, one variable can measure Intelligence Quotient (IQ) test scores and another variable can measure head circumference. These discrepancies can distort the proximity calculations. Using the zscore function, you can convert all the values in the data set to use the same proportional scale. See zscore for more information.
|
For example, consider a data set, X, made up of five objects where each object is a set of x,y coordinates.
You can define this data set as a matrix
X = [1 2;2.5 4.5;2 2;4 1.5;4 2.5]
and pass it to pdist. The pdist function calculates the distance between object 1 and object 2, object 1 and object 3, and so on until the distances between all the pairs have been calculated. The following figure plots these objects in a graph. The distance between object 2 and object 3 is shown to illustrate one interpretation of distance.
Returning Distance Information
The pdist function returns this distance information in a vector, Y, where each element contains the distance between a pair of objects.
Y = pdist(X)
Y =
Columns 1 through 7
2.9155 1.0000 3.0414 3.0414 2.5495 3.3541 2.5000
Columns 8 through 10
2.0616 2.0616 1.0000
To make it easier to see the relationship between the distance information generated by pdist and the objects in the original data set, you can reformat the distance vector into a matrix using the squareform function. In this matrix, element i,j corresponds to the distance between object i and object j in the original data set. In the following example, element 1,1 represents the distance between object 1 and itself (which is zero). Element 1,2 represents the distance between object 1 and object 2, and so on.
squareform(Y)
ans =
0 2.9155 1.0000 3.0414 3.0414
2.9155 0 2.5495 3.3541 2.5000
1.0000 2.5495 0 2.0616 2.0616
3.0414 3.3541 2.0616 0 1.0000
3.0414 2.5000 2.0616 1.0000 0
 | Terminology and Basic Procedure | Defining the Links Between Objects |  |