| Statistics Toolbox |   |
Pairwise distance between observations.
Syntax
Y = pdist(X) Y = pdist(X,'metric') Y = pdist(X,'minkowski',p)
Description
Y = pdist(X)
X, which is treated as m vectors of size n. For a dataset made up of m objects, there are 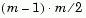 pairs.
pairs.
The output, Y, is a vector of length 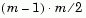 , containing the distance information. The distances are arranged in the order (1,2), (1,3), ..., (1,m), (2,3), ..., (2,m), ..., ..., (m-1,m).
, containing the distance information. The distances are arranged in the order (1,2), (1,3), ..., (1,m), (2,3), ..., (2,m), ..., ..., (m-1,m). Y is also commonly known as a similarity matrix or dissimilarity matrix.
To save space and computation time, Y is formatted as a vector. However, you can convert this vector into a square matrix using the squareform function so that element i,j in the matrix corresponds to the distance between objects i and j in the original dataset.
Y = pdist(X,'metric')
X, using the method specified by 'metric', where 'metric' can be any of the following character strings that identify ways to compute the distance.
| String |
Meaning |
'Euclid' |
Euclidean distance (default) |
'SEuclid' |
Standardized Euclidean distance |
'Mahal' |
Mahalanobis distance |
'CityBlock' |
City Block metric |
'Minkowski' |
Minkowski metric |
Y = pdist(X,'minkowski',p)
X, using the Minkowski metric. p is the exponent used in the Minkowski computation which, by default, is 2.
Mathematical Definitions of Methods
Given an m-by-n data matrix X, which is treated as m (1-by-n) row vectors x1, x2, ..., xm, the various distances between the vector xr and xs are defined as follows:
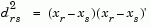
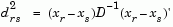
where D is the diagonal matrix with diagonal elements given by
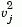 , which denotes the variance of the variable Xj over the m objects.
, which denotes the variance of the variable Xj over the m objects.
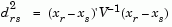
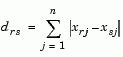
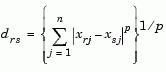
Notice that for the special case of p = 1, the Minkowski metric gives the City Block metric, and for the special case of p = 2, the Minkowski metric gives the Euclidean distance.
Examples
X = [1 2; 1 3; 2 2; 3 1]
X =
1 2
1 3
2 2
3 1
Y = pdist(X,'mahal')
Y =
2.3452 2.0000 2.3452 1.2247 2.4495 1.2247
Y = pdist(X)
Y =
1.0000 1.0000 2.2361 1.4142 2.8284 1.4142
squareform(Y)
ans =
0 1.0000 1.0000 2.2361
1.0000 0 1.4142 2.8284
1.0000 1.4142 0 1.4142
2.2361 2.8284 1.4142 0
See Also
cluster, clusterdata, cophenet, dendrogram, inconsistent, linkage, squareform
 | perms |  |