

| Real-Time Workshop User's Guide |   |
Getting Started
This section illustrates, through a simple example, how to transform a Simulink model into a stand-alone executable program. This program runs independently of Simulink, allowing accelerated execution on the development host or a different target computer.
Generating Ada code from a Simulink model is very similar to generating C code. Begin by typing
countersdemo
at the MATLAB prompt. This block diagram appears.
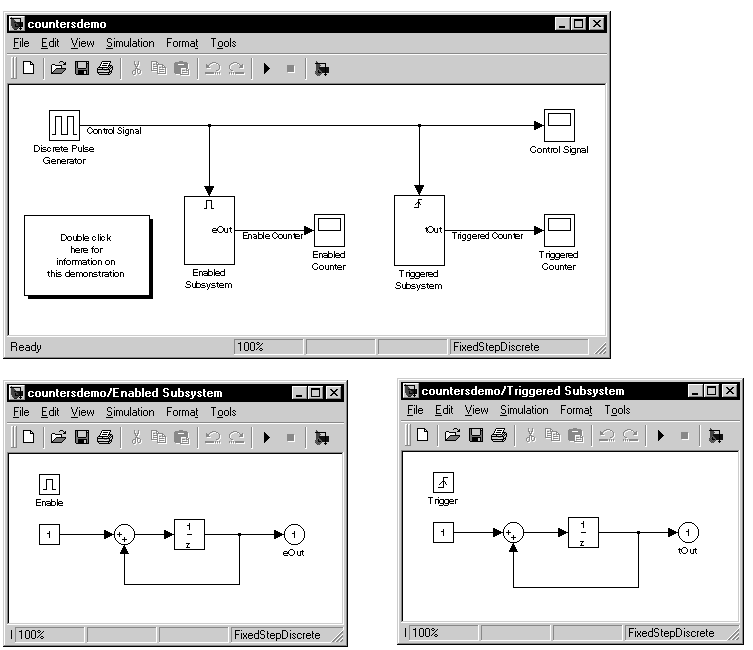
Figure 16-1: Counter Demonstration with Subsystems Open
Setting Options for Ada Code Generation
You must specify the correct options before you generate Ada code from this model. These are the steps:
Figure 16-2 shows the System Target File Browser with the correct selection
for Ada code generation.
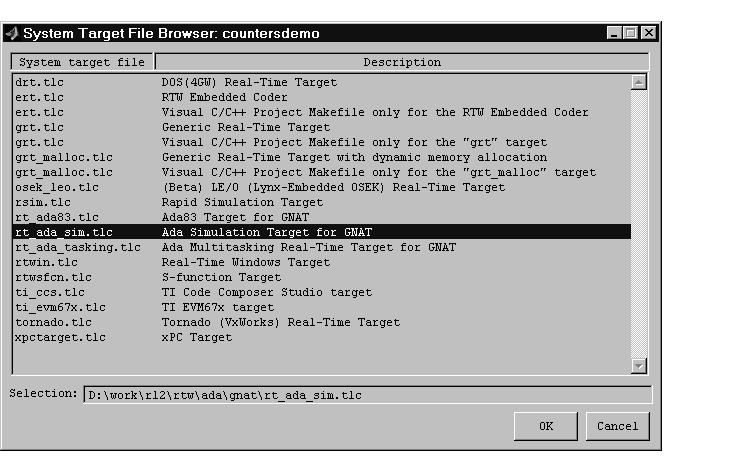
Figure 16-2: The System Target File Browser
Alternatively, you can specify the settings on the Real-Time Workshop page manually by following these steps:
rt_ada_sim.tlc as the System target file.
gnat_sim.tmf as the Template makefile.
make_rtw -ada as the Make command.
Figure 16-3 shows the Real-Time Workshop page with the correct settings.
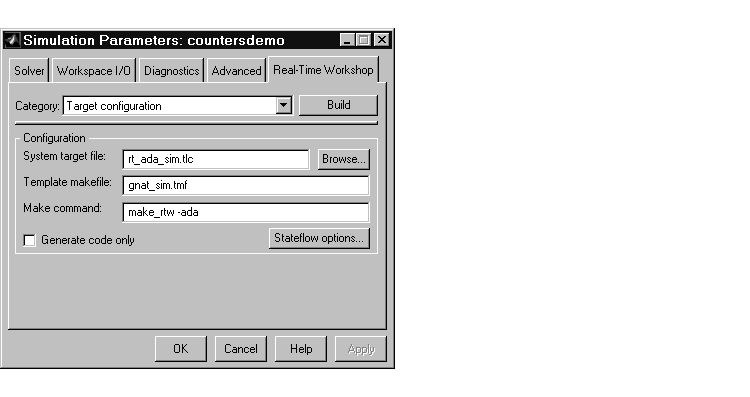
Figure 16-3: Target Configuration Settings in the Real-Time Workshop Page
In addition, you can use the make command to pass compiler switches to the code compilation phase. For example, if you want to compile with debugging symbols, add a -g after the -ada switch in the Make command field (there must be a space between each switch). This switch is applied on a model basis; for more permanent changes, see Configuring the Template Makefile.
Generating Ada Code
To generate Ada code and build an Ada executable, open the Real-Time Workshop page. In the Category menu, select Target configuration. Click the Build button.
Alternatively, select Build Model under the Real-Time Workshop submenu of the Tools menu.
Generated Files
The Real-Time Workshop Ada Coder creates output files in two directories during the build process:
If an executable is created, it is written to your working directory. The executable is named model.exe (on PC) or model (on UNIX).·
The build process creates a subdirectory, called the build directory, within your working directory. The build directory name is model_adaXX_rtw, where model is the name of the source model, and adaXX is either ada83 or ada95, depending on the selected target. The build directory stores generated source code and all other files (other than the executable) created during the build process.
This table lists the Ada files generated by the Real-Time Workshop Ada Coder from the counter demonstration (countersdemo).
 | Restrictions | Models with S-Functions |  |