

| Power System Blockset |   |
Implement a single phase transmission line with lumped parameters.
Library
Description
The PI Section Line block implements a single phase transmission line with parameters lumped in pi sections.
For a transmission line, the resistance, inductance and capacitance are uniformly distributed along the line. An approximate model of the distributed parameter line is obtained by cascading several identical pi sections as shown in the figure below.
Unlike the Distributed Parameter Line block, which has an infinite number of states, the pi section linear model has a finite number of states that permits to compute a linear state-space model. The number of sections to be used depends on the frequency range to be represented.
A good approximation of the maximum frequency range represented by the pi line model is given by the following equation
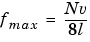
v = Propagation speed in km/s = 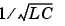 L in H/km, C in F/km
L in H/km, C in F/kmFor example, for a 100 km aerial line having a propagation speed of 300 000 km/s, the maximum frequency range represented with a single pi section is approximately 375 Hz. For studying interactions between a power system and a control system, this simple model could be sufficient. However for switching surge studies involving high frequency transients in the kHz range, much shorter pi sections should be used. In fact, accurate results would probably only be obtained by using a distributed parameters line model.
Dialog Box and Parameters
 ).
).1.Example
Obtain the line energization voltages and current in the following circuit. This circuit is available in the psbpiline.mdl file.
The results obtained with the line modeled by one pi section of 100 km and 10 pi sections of 10 km are shown below.
See Also
Distributed Parameter Line
 | Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machine | Powergui |  |