| Partial Differential Equations Toolbox |   |
PDE Toolbox graphical user interface (GUI).
pdetool pdetool(action,flag)
Description
pdetool
provides the graphical user interface (GUI) for the PDE Toolbox. Call pdetool without arguments to start the application. You should not call pdetool with arguments.
pdetool contains several different modes:
In Draw mode, you construct a Constructive Solid Geometry model (CSG model) of the geometry. You can draw solid objects that can overlap. There are four types of solid objects:
pdetool can be started by just typing the name of the model. (This starts the corresponding M-file that contains the MATLAB commands necessary to create the model.)
The solid objects can be combined by typing a set formula. Each object is automatically assigned a unique name, which is displayed in the GUI on the solid object itself. The names refer to the object in the set formula. More specifically, in the set formula, the name refers to the set of points inside the object. The resulting geometrical model is the set of points for which the set formula evaluates to true. (For a description of the syntax of the set formula, see decsg.) By default, the resulting geometrical model is the union of all objects.
A "snap-to-grid" function is available. This means that objects align to the grid. The grid can be turned on and off, and the scaling and the grid spacing can be changed.
In boundary mode, you can specify the boundary conditions. You can have different types of boundary conditions on different boundaries. In this mode, the original shapes of the solid building objects constitute borders between subdomains of the model. Such borders can be eliminated in this mode. The outer boundaries are color coded to indicate the type of boundary conditions. A red outer boundary corresponds to Dirichlet boundary conditions, blue to generalized Neumann boundary conditions, and green to mixed boundary conditions. You can return to the boundary condition display by clicking on the  button or by selecting Boundary Mode from the Boundary menu.
In PDE mode, you can specify the type of PDE problem, and the coefficients c, a, f, and d. You may specify the coefficients for each subdomain independently. This makes it easy to specify, e.g., various material properties in one PDE model. The PDE to be solved can be specified by clicking on the PDE button or by selecting PDE Specification . . . from the PDE menu. This brings up a dialog box.
In Mesh mode, you can control the automated mesh generation and plot the mesh. An initial mesh can be generated by clicking on the
button or by selecting Boundary Mode from the Boundary menu.
In PDE mode, you can specify the type of PDE problem, and the coefficients c, a, f, and d. You may specify the coefficients for each subdomain independently. This makes it easy to specify, e.g., various material properties in one PDE model. The PDE to be solved can be specified by clicking on the PDE button or by selecting PDE Specification . . . from the PDE menu. This brings up a dialog box.
In Mesh mode, you can control the automated mesh generation and plot the mesh. An initial mesh can be generated by clicking on the  button or by selecting Initialize Mesh from the Mesh menu. The initial mesh can be repeatedly refined by clicking on the refine button or by selecting Refine Mesh from the Mesh menu.
In Solve mode, you can specify solve parameters and solve the PDE. For parabolic and hyperbolic PDE problems, you can also specify the initial conditions, and the times at which the output should be generated. For eigenvalue problems, the search range can be specified. Also, the adaptive and nonlinear solvers for elliptic PDEs can be invoked. The PDE problem is solved by clicking on the = button or by selecting Solve PDE from the Solve menu. By default, the solution is plotted in the
button or by selecting Initialize Mesh from the Mesh menu. The initial mesh can be repeatedly refined by clicking on the refine button or by selecting Refine Mesh from the Mesh menu.
In Solve mode, you can specify solve parameters and solve the PDE. For parabolic and hyperbolic PDE problems, you can also specify the initial conditions, and the times at which the output should be generated. For eigenvalue problems, the search range can be specified. Also, the adaptive and nonlinear solvers for elliptic PDEs can be invoked. The PDE problem is solved by clicking on the = button or by selecting Solve PDE from the Solve menu. By default, the solution is plotted in the pdetool axes.
In Plot mode you can select a wide variety of visualization methods such as surface, mesh, contour, and quiver (vector field) plots. For surface plots, you can choose between interpolated and flat rendering schemes. The mesh can be hidden in all plot types. For parabolic and hyperbolic equations, you can animate the solution as it changes with time. You can show the solution both in 2-D and 3-D. 2-D plots are shown inside pdetool. 3-D plots are plotted in separate figure windows. Different types of plots can be selected by clicking on the button with the solution plot icon or by selecting Parameters . . . from the Plot menu. This opens a dialog box.
In this dialog box, the boundary condition for the selected boundaries is entered.The following boundary conditions can be handled:
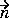 · (c
· (c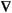 u) + qu = g on the boundary.
u) + qu = g on the boundary.
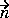 is the outward unit length normal.
The boundary conditions can be entered in a variety of ways. See the entry on
is the outward unit length normal.
The boundary conditions can be entered in a variety of ways. See the entry on assemb and the "Boundary Menu" in the manual.
PDE Specification Dialog BoxIn this dialog box, the type of PDE and the PDE coefficients are entered. The following types of PDEs can be handled:
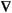 · (c
· (c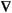 u) + au = f
u) + au = f
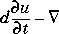 · (c
· (c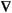 u) + au = f
u) + au = f
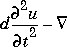 · (c
· (c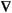 u) + au = f
u) + au = f
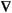 · (c
· (c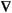 u) + au =
u) + au = 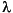 du
du
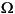 .
The PDE coefficients can be entered in a variety of ways. See the entry on
.
The PDE coefficients can be entered in a variety of ways. See the entry on assempde and the "PDE Menu" in the manual.
The Model M-file contains the MATLAB commands necessary to create a CSG model. It can also contain additional commands to set boundary conditions, define the PDE, create the mesh, solve the pde, and plot the solution. This type of M-file can be saved and opened from the File menu.
The Model M-file is a MATLAB function and not a script. This way name clashes between variables used in the function and in the main workspace are avoided. The name of the file must coincide with the model name. The beginning of the file always looks similar to the code fragment below:
function pdemodel
pdeinit;
pde_fig=gcf;
ax=gca;
pdetool('appl_cb',1);
setuprop(pde_fig,'currparam',str2mat('1.0','0.0','10.0','1.0'))
;
pdetool('snapon');
set(ax,'AspectRatio',[1.5 1]);
set(ax,'XLim',[-1.5 1.5]);
set(ax,'YLim',[-1 1]);
set(ax,'XTickMode','auto');
set(ax,'YTickMode','auto');
grid on;
The pdeinit command starts up pdetool. If pdetool has already been started, the current model is cleared. The following commands set up the scaling and tick marks of the axis of pdetool and other user parameters.
Then a sequence of drawing commands is issued. The commands that can be used are named pdecirc, pdeellip, pdepoly, and pderect. The command sequence below creates the L-shaped membrane as the union of three squares. The solid objects are given names SQ1, SQ2, SQ3, etc.
% Geometry description: pderect([-1 0 0 -1],'SQ1'); pderect([0 1 0 -1],'SQ2'); pderect([0 1 1 0],'SQ3');We do not intend to fully document the format of the Model M-file. It can be used to change the geometry of the drawn objects, since the
pdecirc, pdeellip, pdepoly, and pderect commands are documented.
See Also
initmesh, assempde, parabolic, wave, pdeeig, pdesurf, pdecont
 | pdesurf | pdetrg |  |