| Optimization Toolbox |   |
Find the minimum of a function of one variable on a fixed interval

where x, x1, and x2 are scalars and f(x) is a function that returns a scalar.
Syntax
x = fminbnd(fun,x1,x2) x = fminbnd(fun,x1,x2,options) x = fminbnd(fun,x1,x2,options,P1,P2,...) [x,fval] = fminbnd(...) [x,fval,exitflag] = fminbnd(...) [x,fval,exitflag,output] = fminbnd(...)
Description
fminbnd finds the minimum of a function of one variable within a fixed interval.
x = fminbnd(fun,x1,x2)
returns a value x that is a local minimizer of the scalar valued function that is described in fun in the interval x1 < x < x2.
x = fminbnd(fun,x1,x2,options)
minimizes with the optimization parameters specified in the structure options.
x = fminbnd(fun,x1,x2,options,P1,P2,...)
provides for additional arguments, P1, P2, etc., which are passed to the objective function, fun. Use options=[] as a placeholder if no options are set.
[x,fval] = fminbnd(...)
returns the value of the objective function computed in fun at the solution x.
[x,fval,exitflag] = fminbnd(...)
returns a value exitflag that describes the exit condition of fminbnd.
[x,fval,exitflag,output] = fminbnd(...)
returns a structure output that contains information about the optimization.
Arguments
Input Arguments. Table 4-1, Input Arguments, contains general descriptions of arguments passed in to fminbnd. This section provides function-specific details for fun and options:
fun |
The function to be minimized. fun is a function that accepts a scalar x and returns a scalar f, the objective function evaluated at x. The function fun can be specified as a function handle.x = fminbnd(@myfun,x0)where myfun is a MATLAB function such asfunction f = myfun(x) f = ... % Compute function value at x. fun can also be an inline object.x = fminbnd(inline('sin(x*x)'),x0); |
options |
Options provides the function-specific details for the options parameters. |
Output Arguments. Table 4-2, Output Arguments, contains general descriptions of arguments returned by fminbnd. This section provides function-specific details for exitflag and output:
Options
Optimization options parameters used by fminbnd. You can use optimset to set or change the values of these fields in the parameters structure, options. See Table 4-3, Optimization Options Parameters,, for detailed information:
Examples
x = fminbnd(@sin,0,2*pi)
x =
4.7124
The value of the function at the minimum is
y = sin(x)
y =
-1.0000
To find the minimum of the function
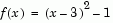
on the interval (0,5), first write an M-file.
function f = myfun(x) f = (x-3).^2 - 1;
Next, call an optimization routine.
x = fminbnd(@myfun,0,5)
x =
3
y = f(x)
y =
-1
Algorithm
fminbnd is an M-file. The algorithm is based on Golden Section search and parabolic interpolation. A Fortran program implementing the same algorithm is given in [1].
Limitations
The function to be minimized must be continuous. fminbnd may only give local solutions.
fminbnd often exhibits slow convergence when the solution is on a boundary of the interval. In such a case, fmincon often gives faster and more accurate solutions.
fminbnd only handles real variables.
See Also
@ (function_handle), fminsearch, fmincon, fminunc, optimset, inline
References
[1] Forsythe, G.E., M.A. Malcolm, and C.B. Moler, Computer Methods for Mathematical Computations, Prentice Hall, 1976.
 | fgoalattain | fmincon |  |