| Communications Toolbox |   |
Reed-Solomon decoding using the exponential format
Syntax
msg = rsdecode(code,k); msg = rsdecode(code,k,m); msg = rsdecode(code,k,field); [msg,err] = rsdecode(...); [msg,err,ccode] = rsdecode(...);
For All Syntaxes
The encoding counterpart for this function is rsencode.
rsdecode uses the exponential format to represent elements of GF(2m). For example, an entry of 2 represents the element 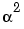 , where
, where 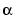 is a primitive element of GF(2m). If
is a primitive element of GF(2m). If field is not used as an input argument, then the exponential format is relative to a root of MATLAB's default primitive polynomial for GF(2m).If field is used as an input argument, then its format and the formats in msg and code are all relative to the same primitive element of GF(2m). See Representing Elements of Galois Fields for more information about these formats.
Since GF(2m) has 2m elements, each codeword represents 2m(2m-1) bits of information. Each decoded message represents 2m*k bits of information.
For Specific Syntaxes
msg = rsdecode(code,k)
decodes code using the Reed-Solomon method. k is the message length. The codeword length n must have the form 2m-1 for some integer m greater than or equal to 3. code is a matrix with n columns. Each row of code represents one codeword. Each entry of code represents an element of GF(2m) in exponential format. msg is a matrix with k columns. Each row of msg represents one message. Each entry of msg is the exponential format of an element of GF(2m).
msg = rsdecode(code,k,m)
is the same as the first syntax when the matrix code has 2m-1 columns. This syntax is faster than the first.
msg = rsdecode(code,k,field)
is the same as the first syntax, except that field is a matrix that lists the elements of GF(2m) in the format described in List of All Elements of a Galois Field. This syntax is faster than the first two.
[msg,err] = rsdecode(...)
returns a column vector err that gives information about error correction. A nonnegative integer in err(r) indicates the number of errors corrected in the rth codeword; a negative integer indicates that there are more errors in the rth codeword than can be corrected.
[msg,err,ccode] = rsdecode(...)
returns the corrected code in ccode.
Examples
The script below continues the example from the reference page for rsencode. After corrupting some symbols from the code, it tries to recover the message.
m = 3; n = 2^m-1; % Codeword length is 7.
field = gftuple([-1:2^m-2]',m,2); % List of elements in GF(2^m)
msg = [5 0 1; 2 3 4];
k = size(msg,2); % Message length = number of columns of msg
genpoly = rspoly(n,k,field); % Generator polynomial
code = rsencode(msg,genpoly,n,field);
% Change up to three of the code symbols.
noisycode = code;
noisycode(1,2) = randint(1,1,[-1,n-1]);
noisycode(2,1) = randint(1,1,[-1,n-1]);
noisycode(2,5) = randint(1,1,[-1,n-1]);
% Try to decode.
[newmsg,err,ccode] = rsdecode(noisycode,k,field);
if ccode==code
disp('All errors were corrected.')
end
if newmsg==msg
disp('The message was recovered perfectly.')
end
Unless one of the random integers was zero, err is the matrix [1;2], which reflects the fact that we put one error in the first row of noisycode and two errors in the second row. Since this code's error-correction capability is floor((n-k)/2), or 2, all errors are corrected in this example.
See Also
rsencode, encode, decode, rsdeco
 | rsdeco | rsdecof |  |