| Statistics Toolbox |   |
Uniform (Continuous) Distribution
The following sections provide an overview of the uniform distribution.
Background of the Uniform Distribution. The uniform distribution (also called rectangular) has a constant pdf between its two parameters a (the minimum) and b (the maximum). The standard uniform distribution (a = 0 and b = 1) is a special case of the beta distribution, obtained by setting both of its parameters to 1.
The uniform distribution is appropriate for representing the distribution of round-off errors in values tabulated to a particular number of decimal places.
Definition of the Uniform Distribution. The uniform cdf is
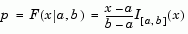
Parameter Estimation for the Uniform Distribution. The sample minimum and maximum are the MLEs of a and b respectively.
Example and Plot of the Uniform Distribution. The example illustrates the inversion method for generating normal random numbers using rand and norminv. Note that the MATLAB function, randn, does not use inversion since it is not efficient for this case.
u = rand(1000,1); x = norminv(u,0,1); hist(x)
 | Noncentral t Distribution | Weibull Distribution |  |