| Stateflow |   |
MATLAB Name Space Operator
The MATLAB name space operator, ml, is used to get and set variables in the MATLAB workspace. The ml operator can also be used to access MATLAB functions that operate on scalars in a convenient format.
Use the notation, a = ml.func_name();, to call a MATLAB function that does not accept any arguments. Omission of the empty brackets causes a search for a variable of the name specified. The variable will not be found and a runtime error is encountered during simulation.
Use of the ml name space operator should be avoided if you plan to build a Real-Time Workshop target that includes code from Stateflow Coder.
Example: Using the ml Operator to Access MATLAB Workspace Variables
This is an example of using the ml operator to get and set variables in the MATLAB workspace.
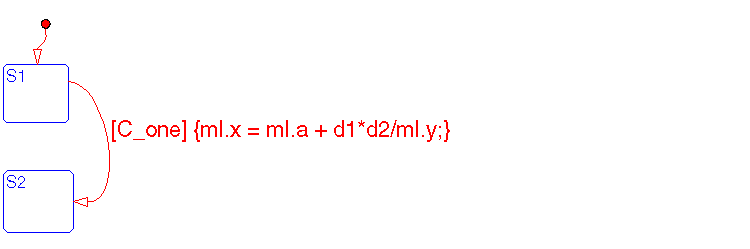
These data objects are defined in the Stateflow diagram:
d1 and d2 are Local data objects a, x, and y must be defined in the MATLAB workspace prior to starting the simulation; otherwise a runtime error is generated at the execution time of the transitionThe values of a and y are accessed in the MATLAB workspace and used in the expression with the Local data objects d1 and d2. The result of the expression is assigned to the MATLAB workspace variable x. If x does not exist, it is automatically created in the MATLAB workspace.
Example: Using the ml Operator to Access MATLAB Functions
This is an example of using the ml operator to access MATLAB functions.

These data objects are defined:
1 and d2 are Local data objects defined in the Stateflow diagramx is assumed to be a two dimensional array in the MATLAB workspacey is assumed to be a MATLAB workspace vector. z is assumed to be a MATLAB workspace scalar variable.x, y, and z must be defined in the MATLAB workspace prior to starting the simulation; otherwise a runtime error is generated at the execution time of the transition.
A MATLAB function named my_func is called with these arguments:
The result of my_func() (if it is a scalar) is assigned to element (5, 6, 7) of a multidimensional matrix v in the MATLAB workspace. If v does not exist prior to the execution of this statement, then it is automatically created by MATLAB workspace.
If my_func() returns a vector, the first element is assigned to v(5,6,7). If it is a structure, a cell array, or a string, the result is undefined.
 | ml() Functions | The ml() Function Versus ml Name Space Operator |  |