| Stateflow |   |
ml() Functions
You can specify calls to MATLAB functions that return scalars (of type double) in the action language.
ml() Function Format
The format of the ml() function is
ml(evalString, arg1, arg2, arg3,...);
where the return value is scalar (of type double).
evalString is a string that is evaluated in the MATLAB workspace with formatted substitutions of arg1, arg2, arg3, etc.
Example One: ml() Function Call
This is an example of an ml() function call as part of a condition action.
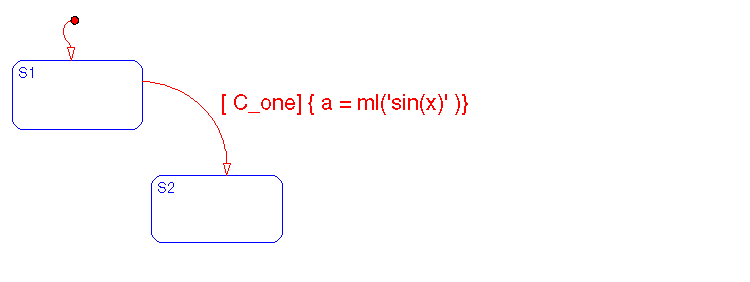
If S1 is active, an event occurs, and if [c_one] is true, the expression sin(x) is evaluated in the MATLAB workspace and the return value assigned to a. (x must be a variable in the MATLAB workspace and a is a data object in the Stateflow diagram). The result of the evaluation must be a scalar. If x is not defined in the MATLAB workspace, a runtime error is generated.
Example Two: ml() Function Call
This is an example of a ml() function call that passes Stateflow data as arguments. Notice the use of format specifiers %g and %d as are used in the C language function printf.
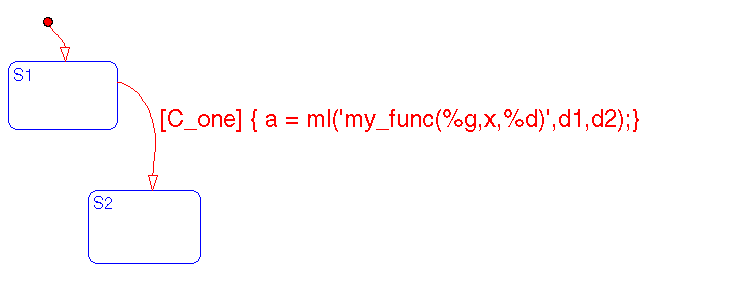
These data objects are defined:
d1 and a are Local data objects of type double in the Stateflow diagramd2 is an Output to Simulink data object of type integer in the Stateflow diagramThese three values are passed as arguments to a user-written function. The %g and %d characters are format specifiers that print the current values of d1 and d2 into evalString at appropriate locations.
For example if d1 equals 3.4 and d2 equals 5, using the format specifiers these are mapped into my_func(3.4,x,5). This string is then sent to MATLAB and is executed in the MATLAB workspace.
Example Three: ml() Function Call
This is an example of a ml() function call with string arguments.

These data objects are defined in the Stateflow diagram:
d1 is a Local data object of type double d2 is an Output to Simulink data object of type integer The user-written function my_string_func expects four arguments, where the second argument is a string. The %g and %d characters are format specifiers that print the current values of d1 and d2 into evalString at appropriate locations. Notice that the string is enclosed in two single quotes.
Use Guidelines
These guidelines apply to ml() functions:
printf.ml() functions should be avoided if you plan to build an RTW target that includes code from Stateflow Coder. | User-Written Functions | MATLAB Name Space Operator |  |