
| Signal Processing Toolbox |   |
One-dimensional inverse fast Fourier transform.
Syntax
y=ifft(x) y=ifft(x,n)
Description
ifft computes the inverse Fourier transform of a vector or array. This function implements the inverse transform given by
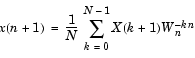
where WN = e-j(2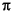 /N) and N
/N) and N = length(x). Note that the series is indexed as n + 1 and k + 1 instead of the usual n and k because MATLAB vectors run from 1 to N instead of from 0 to N-1.
y is the inverse Fourier transform of vector = ifft(x)
x. If x is an array, y is the inverse FFT of each column of the matrix.
y is the = ifft(x,n)
n-point inverse FFT. If the length of x is less than n, ifft pads x with trailing zeros to length n. If the length of x is greater than n, ifft truncates the sequence x. When x is an array, ifft adjusts the length of the columns in the same manner.
The ifft function is part of the standard MATLAB language.
Algorithm
The ifft function is an M-file. The algorithm for ifft is the same as that for fft, except for a sign change and a scale factor of n = length(x). The execution time is fastest when n is a power of two and slowest when n is a large prime.
See Also
|
One-dimensional fast Fourier transform. |
|
Two-dimensional fast Fourier transform. |
|
Rearrange the outputs of fft and fft2. |
|
Two-dimensional inverse fast Fourier transform. |
 | idct | ifft2 |  |