
| Signal Processing Toolbox |   |
Syntax
p = angle(h)
Description
p = angle(h)
returns the phase angles, in radians, of the elements of complex vector or array h. The phase angles lie between -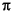 and
and 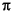 .
.
For complex sequence h = x + iy = meip, the magnitude and phase are given by
m=abs(h) p=angle(h)
To convert to the original h from its magnitude and phase, type
i=sqrt(-1) h=m.*exp(i*p)
The angle function is part of the standard MATLAB language.
Example
Calculate the phase of the FFT of a sequence.
t=(0:99)/100; % time vector x=sin(2*pi*15*t) + sin(2*pi*40*t); % signal y=fft(x); % compute DFT of x p=unwrap(angle(y)); % phase
f=(0:length(y)-1)'/length(y)*100; % frequency vector plot(f,p)
Algorithm
angle(x)=imag(log(x))=atan2(imag(x),real(x))
See Also
|
Absolute value (magnitude). |
 | ac2rc | arburg |  |