

| Real-Time Workshop User's Guide |   |
General Code Generation Options
These options are common to all target configurations.
Show Eliminated Statements Option
If this option is selected, statements that were eliminated as the result of optimizations (such as parameter inlining) appear as comments in the generated code.
Loop Rolling Threshold Field
The loop rolling threshold determines when a wide signal or parameter should be wrapped into a for loop and when it should be generated as a separate statement for each element of the signal. The default threshold value is 5.
For example, consider the model below

The gain parameter of the Gain block is the vector myGainVec.
Assume that the loop rolling threshold value is set to the default, 5.
myGainVec = [1:10];
an array of 10 elements, rtP.Gain_Gain[] is declared within the Parameters data structure, rtP. The size of the gain array exceeds the loop rolling threshold. Therefore the code generated for the Gain block iterates over the array in a for loop, as shown in the following code fragment.
/* Gain Block: <Root>/Gain */
{
int_T i1;
real_T *y0 = &rtB.Gain[0];
const real_T *p_Gain_Gain = &rtP.Gain_Gain[0];
for (i1=0; i1 < 10; i1++) {
y0[i1] = rtb_foo * (p_Gain_Gain[i1]);
}
}
myGainVec = [1:3];
an array of 3 elements, rtP.Gain_Gain[] is declared within the Parameters data structure, rtP. The size of the gain array is below the loop rolling threshold. The generated code consists of inline references to each element of the array, as in the code fragment below.
/* Gain Block: <Root>/Gain */ rtB.Gain[0] = rtb_foo * (rtP.Gain_Gain[0]); rtB.Gain[1] = rtb_foo * (rtP.Gain_Gain[1]); rtB.Gain[2] = rtb_foo * (rtP.Gain_Gain[2]);
See the Target Language Compiler Reference Guide for more information on loop rolling.
Verbose Builds Option
If this option is selected, the MATLAB command window displays progress information during code generation; compiler output is also made visible.
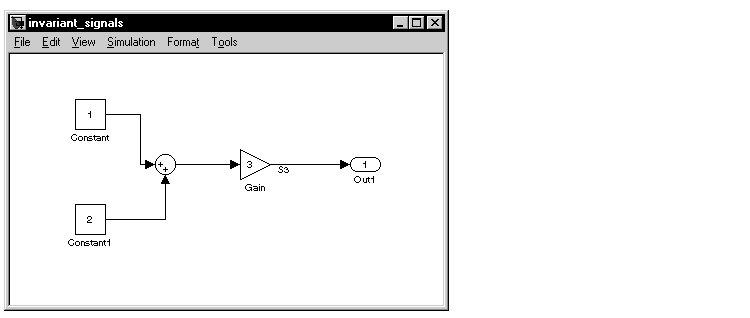
Inline Invariant Signals Option
An invariant signal is a block output signal that does not change during Simulink simulation. For example, the signal S3 in this block diagram is an invariant signal.
| Note The Inline invariant signals option is unavailable unless the Inline parameters option (on the Advanced page) is selected. |
Given the model above, if both Inline parameters and Inline invariant signals is selected, the Real-time Workshop inlines the invariant signal S3 in the generated code.
Note that an invariant signal is not the same as an invariant constant. (See the Using Simulink manual for information on invariant constants.) In the above example, the two constants (1 and 2) and the gain value of 3 are invariant constants. To inline these invariant constants, select Inline parameters.
Local Block Outputs Option
When this option is selected, block signals will be declared locally in functions instead of being declared globally (when possible).
| Note This check box is disabled when the Signal storage reuse item on the Advanced page is turned off. |
For further information on the use of the Local block outputs option, see:
Force Generation of Parameter Comments Option
The Force generation of parameter comments option controls the generation of comments in the model parameter structure declaration in model_prm.h. Parameter comments indicate parameter variable names and the names of source blocks.
When this option is off (the default), parameter comments are generated if less than 1000 parameters are declared. This reduces the size of the generated file for models with a large number of parameters.
When this option is on, parameter comments are generated regardless of the number of parameters.
 | Target Configuration Options | Target Specific Code Generation Options |  |