

| Real-Time Workshop User's Guide |   |
Tutorial 4: A First Look at Generated Code
In this tutorial, you examine code generated from a from a simple model, to observe the effects of one of the many code optimization features available in the Real-Time Workshop.
Figure 1-12 shows the source model.

Setting up the Model
First, create the model and set up basic Simulink and Real-Time Workshop parameters as follows:
example_codegen, and make it your working directory.
!mkdir example_codegencd example_codegen
example.mdl.
Solver options: set Type to Fixed-step. Select the ode5 (Dormand-Prince)
solver algorithm.
Leave the other Solver page parameters set to their default values.
make to compile and link the code. This option is convenient for this exercise, as we are only interested in looking at the generated code. Note that the Build button caption changes to Generate code.
Also, make sure that the generic real-time (GRT) target is selected. The page should appear as below.
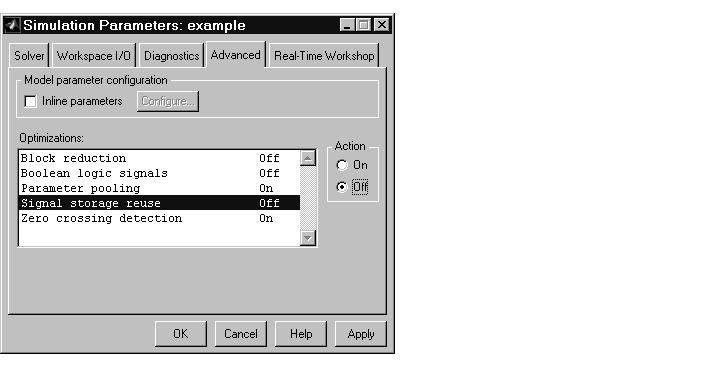
Generating Code Without Buffer Optimization
When the block I/O optimization feature is enabled, the Real-Time Workshop uses local storage for block outputs wherever possible. We now disable this option to see what the generated code looks like:
### Successful completion of Real-Time Workshop build procedure
for model: example
example_grt_rtw. The file example_grt_rtw\example.c contains the output computation for the model. Open this file into the MATLAB editor.
edit example_grt_rtw\example.c
example.c, find the function MdlOutputs.
The generated C code consists of procedures that implement the algorithms defined by your Simulink block diagram. Your target's execution engine executes the procedures as time moves forward. The modules that implement the execution engine and other capabilities are referred to collectively as the run-time interface modules.
In our example, the generated MdlOutputs function implements the actual algorithm for multiplying a sine wave by a gain. The MdlOutputs function computes the model's block outputs. The run-time interface must call MdlOutputs at every time step.
With buffer optimizations turned off, MdlOutputs assigns buffers to each block input and output. These buffers (rtB.sin_out, rtB.gain_out) are members of a global data structure, rtB. The code is shown below.
void MdlOutputs(int_T tid)
{
/* Sin Block: <Root>/Sine Wave */
rtB.sin_out = rtP.Sine_Wave_Amp *
sin(rtP.Sine_Wave_Freq * ssGetT(rtS) + rtP.Sine_Wave_Phase);
/* Gain Block: <Root>/Gain */
rtB.gain_out = rtB.sin_out * rtP.Gain_Gain;
/* Outport Block: <Root>/Out1 */
rtY.Out1 = rtB.gain_out;
}
We now turn buffer optimization on and observe how it improves the code.
Generating Code with Buffer Optimization
Enable buffer optimization and re-generate the code as follows:
example_grt_rtw directory. Note that the previously-generated code is overwritten.
example_grt_rtw/example.c, and examine the function MdlOutputs.
With buffer optimization enabled, the code in MdlOutputs reuses rtb_temp0, a temporary buffer with local scope, rather than assigning global buffers to each input and output.
void MdlOutputs(int_T tid)
{
/* local block i/o variables */
real_T rtb_temp0;
/* Sin Block: <Root>/Sine Wave */
rtb_temp0 = rtP.Sine_Wave_Amp *
sin(rtP.Sine_Wave_Freq * ssGetT(rtS) + rtP.Sine_Wave_Phase);
/* Gain Block: <Root>/Gain */
rtb_temp0 *= rtP.Gain_Gain;
/* Outport Block: <Root>/Out1 */
rtY.Out1 = rtb_temp0;
}
This code is more efficient in terms of memory usage. The efficiency improvement gained by enabling Local block outputs would be more significant in a large model with many signals.
Note that, by default, Local block outputs is enabled. Chapter 3, Code Generation and the Build Process contains details on this and other code generation options.
For further information on the structure and execution of model.c files, refer to Chapter 6, Program Architecture.
 | Tutorial 3: Code Validation | Where to Find Information in This Manual |  |