

| Real-Time Workshop User's Guide |   |
Storage Classes of Tunable Parameters
The Real-Time Workshop defines four storage classes for tunable parameters. You must declare a tunable parameter to have one of the following storage classes:
SimulinkGlobal(Auto): SimulinkGlobal(Auto) is the default storage class. The Real-Time Workshop stores the parameter as a member of rtP. Each member of rtP is initialized to the value of the corresponding workspace variable at code generation time.ExportedGlobal: The generated code instantiates and initializes the parameter and model_export.h exports it as a global variable. An exported global variable is independent of the rtP data structure. Each exported global variable is initialized to the value of the corresponding workspace variable at code generation time.ImportedExtern: model.h declares the parameter as an extern variable. Your code must supply the proper variable definition and initializer, if any.ImportedExternPointer: model.h declares the variable as an extern pointer. Your code must supply the proper pointer variable definition and initializer, if any.As an example of how the storage class declaration affects the code generated for a parameter, consider the model shown below.
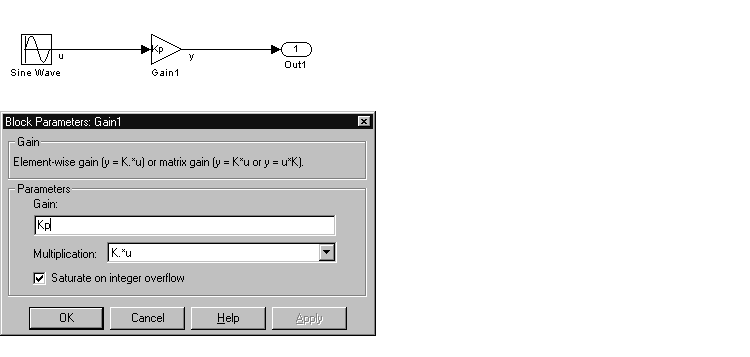
The workspace variable Kp sets the gain of the Gain1 block. Assume that the value of Kp is 5.0. Table 3-3 shows the variable declarations and the code generated for the gain block when Kp is declared as a tunable parameter. An example is shown for each storage class.
Note that the symbolic name Kp is preserved in the variable and field names in the generated code.
 | Tunable Parameter Storage | Using the Model Parameter Configuration Dialog |  |