

| Power System Blockset |   |
Description of the HVDC Transmission System
This network is available as a demo entitled Complete 12-Pulse HVDC Transmission System. Open this demo and save the psbhvdc12pulse.mdl file in your working directory as case5 in order to allow further modifications to the original system.This system is shown on Figure 2-28.
A 1000 MW (500 kV, 2kA) DC interconnection is used to transmit power from a 500 kV, 5000 MVA, 60Hz network to a 345 kV, 10 000MVA, 50Hz network. The AC networks are represented by damped L-R equivalents with an angle of 80 degrees at fundamental frequency (60 Hz or 50 Hz) and at the third harmonic.
The rectifier and the inverter are 12-pulse converters using two Universal Bridge blocks connected in series. Open the two converter subsystems to see how they are built. The converters are interconnected through a 300 km distributed parameter line and 0.5 H smoothing reactors.The converter transformers (Wye grounded /Wye/Delta) are modeled with Three-Phase Transformer (Three-Windings). The transformer tap changers are not simulated. The tap position is rather at a fixed position determined by a multiplication factor applied on the primary nominal voltage of the converter transformers (0.90 on rectifier side; 0.96 on inverter side).
From the AC point of view, an HVDC converter acts as a source of harmonic currents. From the DC point of view, it is a source of harmonic voltages. The order n of these characteristic harmonics are related to the pulse number p of the converter configuration: n = kp ± 1 for the AC current, and n = kp for the direct voltage, k being any integer. In our example, p = 12, so that injected harmonics on the AC side are: 11, 13, 23, 25, and on the DC side are: 12, 24.
AC filters are used to prevent the odd harmonic currents from spreading out on the network. The filters are grouped in two subsystems. These filters also appear as large capacitors at fundamental frequency, thus providing reactive power compensation for the rectifier consumption due to the firing angle 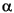 . For
. For 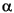 =30 degrees, the converter reactive power demand is approximately 60% of the power transmitted at full load. Look under the AC filters subsystem mask to see the high Q (100) tuned filters at the 11th and 13th harmonic and the low Q (3), or damped filter, used to eliminate the higher order harmonics, e.g., 23rd and up. Extra reactive power is also provided by capacitor banks.
=30 degrees, the converter reactive power demand is approximately 60% of the power transmitted at full load. Look under the AC filters subsystem mask to see the high Q (100) tuned filters at the 11th and 13th harmonic and the low Q (3), or damped filter, used to eliminate the higher order harmonics, e.g., 23rd and up. Extra reactive power is also provided by capacitor banks.
Two circuit breakers are used to apply faults on the rectifier AC and DC sides.
The rectifier and inverter control systems use the Discrete 12-pulse HVDC Control block of the Control library of powerlib_extras.
The power system and the control system are both discretized with the same sample time Ts.
Define parameter Ts=50e-6 in your workspace prior to start simulations.
 | HVDC System | Frequency Response of the AC and DC Systems |  |