

| Power System Blockset |   |
Implement a separately excited DC machine.
Library
Description
This block implements a separately excited DC machine. An access is provided to the field connections (F+, F-) so that the machine model can be used as a shunt-connected or a series-connected DC machine.
The armature circuit (A+, A-) consist of an inductor La and resistor Ra in series with a counter electromotive force (CEMF) E.
The CEMF is proportional to the machine speed:
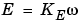
KE is the voltage constant and 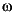 is the machine speed.
is the machine speed.
In a separately excited DC machine model, the voltage constant KE is proportional to the field current if
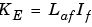
where Laf is the field-armature mutual inductance.
The electromechanical torque developed by the DC machine is proportional to the armature current Ia
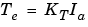
where KT is the torque constant. The sign convention for Te is:
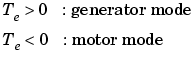
The torque constant is equal to the voltage constant:
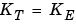
The armature circuit and the field circuit of the DC machine model are built with blocks from powerlib library. The armature circuit is connected between the input port A+ and the output port A- of the DC Machine block. It is represented by a Series RLC Branch block in series with a Controlled Voltage Source and a Current Measurement block.
The field circuit is represented by an RL circuit. It is connected between the input port F+ and the output ports F- of the DC Machine block.
The mechanical part computes the speed of the DC machine from the net torque applied to the rotor. The speed is used to implement the CEMF voltage E of the armature circuit.
The mechanical part is represented by Simulink blocks that implement the equation:
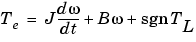
Measurements
Four internal signals are multiplexed on the Simulink measurement output vector (third block output) returning:
Dialog Box
Example
The following circuit illustrates the starting of a 5 HP 240 V DC Machine with a three-step resistance starter. The circuit is available in the psbdcmotor.mdl demo
The Motor Starter subsystem is:
Reference
Reference Analysis of Electric Machinery, Krause and al., pp. 89-92.
See Also
Asynchronous Machine, Synchronous Machine
 | Current Measurement | DC Voltage Source |  |