| Communications Blockset |   |
Create a Reed-Solomon code from binary vector data
Library
Block sublibrary of Channel Coding
Description
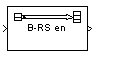
The Binary-Input RS Encoder block creates a Reed-Solomon code with message length K and codeword length N. You specify both N and K directly in the block mask. N must have the form 2M-1, where M is an integer greater than or equal to 3. The code is more efficient if N-K is an even integer.
The input and output are binary-valued signals that represent messages and codewords, respectively. The input must contain exactly M*K elements. If it is frame-based, then it must be a column vector. The output is a vector of length M*N.
The M*K input bits represent K integers between 0 and 2M-1, where more significant bits are to the right. Similarly, the M*N output bits represent N integers between 0 and 2M-1. These integers in turn represent elements of the finite field GF(2M).
An (N,K) Reed-Solomon code can correct up to floor((N-K)/2) symbol errors (not bit errors) in each codeword.
Examples
Suppose M = 3, N = 23-1 = 7, and K = 5. Then a message is a binary vector of length 15 that represents 5 three-bit integers. A corresponding codeword is a binary vector of length 21 that represents 7 three-bit integers. The figure below shows the codeword that would result from a particular message word. The integer format equivalents illustrate that the highest-order bit is at the right.
Dialog Box
Pair Block
See Also
 | Binary Cyclic Encoder | Binary Linear Decoder |  |