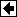
General Notation
|
Interpretation
|
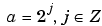
|
Dyadic scale. j is the level, 1/a or 2-j is the resolution
|
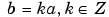
|
Dyadic translation
|
t
|
Continuous time
|
k or n
|
Discrete time
|
(i, j)
|
Pixel
|
s
|
Signal or image. The signal is a function defined on R or Z, the image is defined on R2 or Z2
|
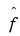
|
Fourier transform of the function f or the sequence f
|
Continuous Time
|
|
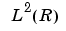
|
Set of signals of finite energy
|
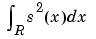
|
Energy of the signal s
|
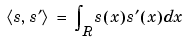
|
Scalar product of signals s and 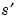
|
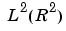
|
Set of images of finite energy
|
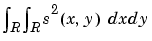
|
Energy of the image s
|
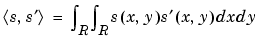
|
Scalar product of images s and 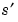
|
Discrete Time
|
|
l2(Z)
|
Set of signals of finite energy
|
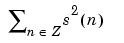
|
Energy of the signal s
|
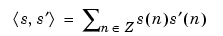
|
Scalar product of signals s and 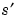
|
l2(Z2)
|
Set of images of finite energy
|
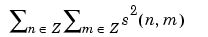
|
Energy of the image s
|
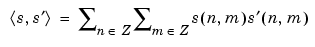
|
Scalar product of images s and 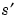
|
Wavelet Notation
|
Interpretation
|
Aj
|
j-level approximation or approximation at level j
|
Dj
|
j-level detail or detail at level j
|
|
Scaling function
|
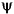
|
Wavelet
|
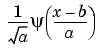
|
Family associated with the one-dimensional wavelet, indexed by 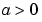 and and 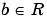 . .
|
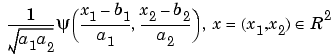
|
Family associated with the two-dimensional wavelet, indexed by
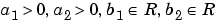
|
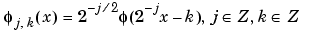
|
Family associated with the one-dimensional scaling function for dyadic scales a = 2j, b = ka; It should be noted that 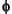 = = 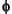 0,0 0,0
|
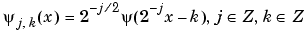
|
Family associated with the one-dimensional 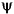 for dyadic scales a = 2j, b = ka; It should be noted that for dyadic scales a = 2j, b = ka; It should be noted that 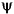 = = 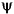 0,0 0,0
|
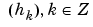
|
Scaling filter associated with a wavelet
|
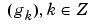
|
Wavelet filter associated with a wavelet
|