| Wavelet Toolbox |   |
The Continuous Wavelet Transform
Mathematically, the process of Fourier analysis is represented by the Fourier transform:

which is the sum over all time of the signal f(t) multiplied by a complex exponential. (Recall that a complex exponential can be broken down into real and imaginary sinusoidal components.)
The results of the transform are the Fourier coefficients 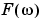 , which when multiplied by a sinusoid of frequency
, which when multiplied by a sinusoid of frequency 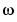 , yield the constituent sinusoidal components of the original signal. Graphically, the process looks like:
, yield the constituent sinusoidal components of the original signal. Graphically, the process looks like:
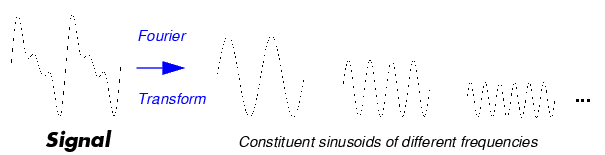
Similarly, the continuous wavelet transform (CWT) is defined as the sum over all time of the signal multiplied by scaled, shifted versions of the wavelet function 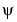 :
:
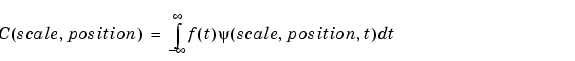
The result of the CWT are many wavelet coefficients C, which are a function of scale and position.
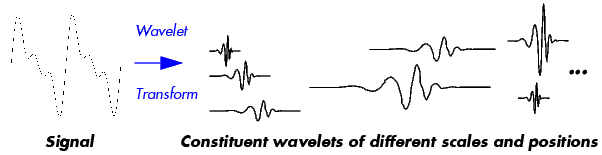
Multiplying each coefficient by the appropriately scaled and shifted wavelet yields the constituent wavelets of the original signal:
 | Number of Dimensions | Scaling |  |