| Symbolic Math Toolbox |   |
Syntax
F = fourier(f) F = fourier(f,v) F = fourier(f,u,v)
Description
F = fourier(f) is the Fourier transform of the symbolic scalar f with default independent variable x. The default return is a function of w. The Fourier transform is applied to a function of x and returns a function of w.
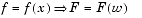
f = f(w), fourier returns a function of t.
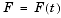
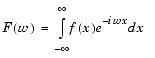
x is the symbolic variable in f as determined by findsym.
F = fourier(f,v) makes F a function of the symbol v instead of the default w.
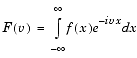
F = fourier(f,u,v) makes f a function of u and F a function of v instead of the default variables x and w, respectively.
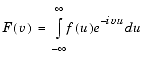
Examples
See Also
ifourier, laplace, ztrans
 | fortran | funtool |  |