| Stateflow |   |
Directed Event Broadcasting
You can specify a directed event broadcast in the action language. Using a directed event broadcast, you can broadcast a specific event to a specific receiver state. Directed event broadcasting is a more efficient means of synchronization amongst AND (parallel) states. Using directed event broadcasting improves the efficiency of the generated code. As is true in event broadcasting, recursive event broadcasts can lead to definition of cyclic behavior.
The format of the directed broadcast is
send(event_name,state_name)
where event_name is broadcast to state_name (and any offspring of that state in the hierarchy). The state_name argument can include a full hierarchy path. For example,
send(event_name, chart_name.state_name1.state_name2)
The state_name specified must be active at the time the send is executed for the state_name to receive and potentially act on the directed event broadcast.
Example: Directed Event Broadcast Using send
This is an example of a directed event broadcast using the send(event_name,state_name) transition action as a transition action.
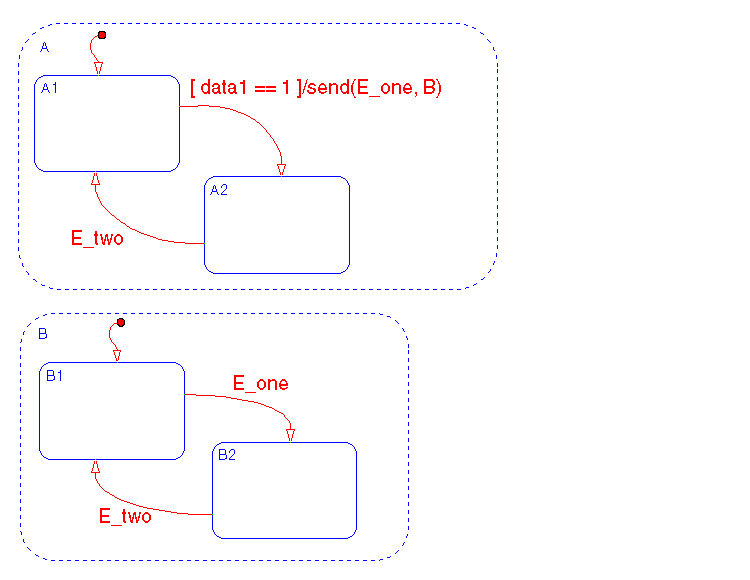
In this example, event E_one must be visible in both A and B. See Example: Directed Event Broadcasting Using Qualified Event Names for information on the semantics of this notation.
Example: Directed Event Broadcast Using Qualified Event Names
This example illustrates use of a qualified event name to in an event broadcast.
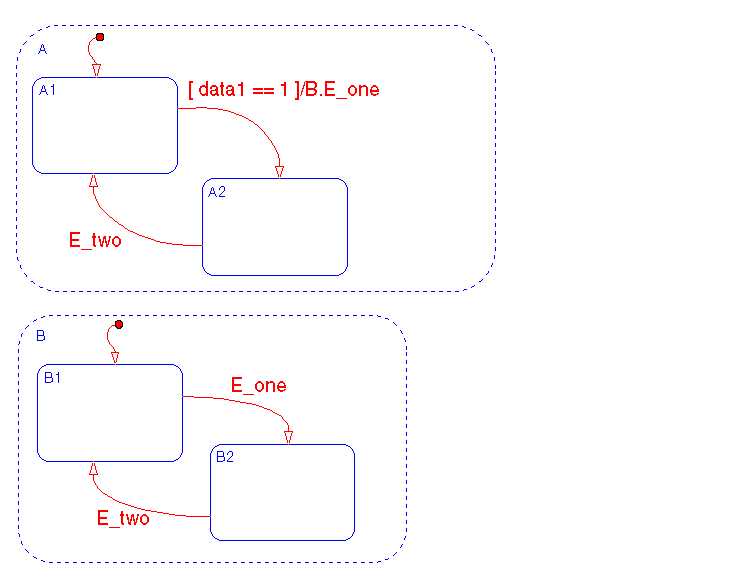
See Example: Directed Event Broadcasting Using Qualified Event Names for information on the semantics of this notation.
 | Pointer and Address Operators | Conditions |  |