| Using Simulink |   |
Implement a transfer function specified in terms of poles and zeros.
Library
Description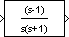
The Zero-Pole block implements a system with the specified zeros, poles, and gain in terms of the Laplace operator s.
A transfer function can be expressed in factored or zero-pole-gain form, which, for a single-input single-output system in MATLAB, is
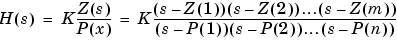
where Z represents the zeros vector, P the poles vector, and K the gain. Z can be a vector or matrix, P must be a vector, K can be a scalar or vector whose length equals the number of rows in Z. The number of poles must be greater than or equal to the number of zeros. If the poles and zeros are complex, they must be complex conjugate pairs.
Block input and output widths are equal to the number of rows in the zeros matrix.
The Zero-Pole Block Icon
The Zero-Pole block displays the transfer function in its icon depending on how the parameters are specified:
For example, if you specify Zeros as [3,2,1], Poles as (poles), where poles is defined in the workspace as [7,5,3,1], and Gain as gain, the icon looks like this: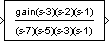
(s)" if appropriate. For example, if you specify Zeros as zeros, Poles as poles, and Gain as gain, the icon looks like this.
Data Type Support
A Zero-Pole block accepts real signals of type double.
Parameters and Dialog Box
[1].[0 -1].[1].Characteristics
| Direct Feedthrough |
Only if the lengths of the Poles and Zeros parameters are equal |
| Sample Time |
Continuous |
| Scalar Expansion |
No |
| States |
Length of Poles vector |
| Dimensionalized |
No |
| Zero Crossing |
No |
 | Zero-Order Hold | Model Construction Commands |  |