| Using Simulink |   |
Library
Description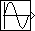
The Sine Wave block provides a sinusoid. The block can operate in either continuous or discrete mode.
The output of the Sine Wave block is determined by
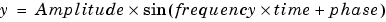
The value of the Sample time parameter determines whether the block operates in continuous mode or discrete mode:
0 (the default) causes the block to operate in continuous mode.>0 causes the block to operate in discrete mode.-1 causes the block to operate in the same mode as the block receiving the signal.Using the Sine Wave Block in Discrete Mode
A Sample time parameter value greater than zero causes the block to behave as if it were driving a Zero-Order Hold block whose sample time is set to that value.
Using the Sine Wave block in this way allows you to build models with sine wave sources that are purely discrete, rather than models that are hybrid continuous/discrete systems. Hybrid systems are inherently more complex and, as a result, take longer to simulate.
The Sine Wave block in discrete mode uses an incremental algorithm rather than one based on absolute time. As a result, the block can be useful in models intended to run for an indefinite length of time, such as in vibration or fatigue testing.
The incremental algorithm computes the sine based on the value computed at the previous sample time. This method makes use of the following identities.
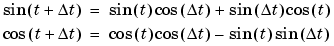
These identities can be written in matrix form.
Since 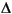 t is constant, the following expression is a constant.
t is constant, the following expression is a constant.
Therefore the problem becomes one of a matrix multiply of the value of sin(t) by a constant matrix to obtain sin(t+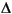 t).
t).
Using the Sine Wave Block in Continuous Mode
A Sample time parameter value of zero causes the block to behave in continuous mode. When operating in continuous mode, the Sine Wave block can become inaccurate due to loss of precision as time becomes very large.
The block's numeric parameters must be of the same dimensions after scalar expansion. If the Interpret vector parameters as 1-D option is off, the block outputs a signal of the same dimensions and dimensionlity as the parameters. If the Interpret vector parameters as 1-D option is on and the numeric parameters are row or column vectors (i.e., single row or column 2-D arrays), the block outputs a vector (1-D array) signal; otherwise, the block outputs a signal of the same dimensionality and dimensions as the parameters.
Data Type Support
A Sine Wave block accepts and outputs real signals of type double.
Parameters and Dialog Box
1.1 rad/sec.0 radians.0.If selected, column or row matrix values for the Sine Wave block's numeric parameters result in a vector output signal; otherwise, the block outputs a signal of the same dimensionality as the parameters. If this option is not selected, the block always outputs a signal of the same dimensionality as the block's numeric parameters.
Characteristics
| Sample Time |
Continuous, discrete, or inherited |
| Scalar Expansion |
Of parameters |
| Dimensionalized |
Yes |
| Zero Crossing |
No |
 | Signal Specification | Slider Gain |  |