
| Signal Processing Toolbox |   |
Syntax
y = sinc(x)
Description
sinc computes the sinc function of an input vector or array, where the sinc function is
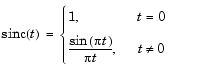
This function is the continuous inverse Fourier transform of the rectangular pulse of width 2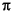 and height 1.
and height 1.
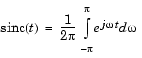
y = sinc(x)
y the same size as x, whose elements are the sinc function of the elements of x.
The space of functions bandlimited in the frequency range 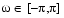 is spanned by the infinite (yet countable) set of sinc functions shifted by integers. Thus any such bandlimited function g(t) can be reconstructed from its samples at integer spacings.
is spanned by the infinite (yet countable) set of sinc functions shifted by integers. Thus any such bandlimited function g(t) can be reconstructed from its samples at integer spacings.
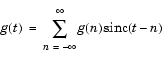
Example
Perform ideal bandlimited interpolation by assuming that the signal to be interpolated is 0 outside of the given time interval and that it has been sampled at exactly the Nyquist frequency.
t=(1:10)'; % A column vector of time samples randn('state',0); x=randn(size(t)); % A column vector of data ts=linspace(-5,15,600)'; % times at which to interpolate data y=sinc(ts(:,ones(size(t))) - t(:,ones(size(ts)))')*x; plot(t,x,'o',ts,y)
See Also
|
Generate a swept-frequency cosine. |
|
Compute the Cosine of vector/matrix elements (see the MATLAB documentation). |
|
Compute the Dirichlet or periodic sinc function. |
|
Generate a Gaussian-modulated sinusoidal pulse. |
|
Generate a pulse train. |
|
Generate a sampled aperiodic rectangle. |
|
Generate a sawtooth or triangle wave. |
|
Compute the sine of vector/matrix elements (see the MATLAB documentation). |
|
Generate a square wave. |
|
Generate a sampled aperiodic triangle. |
 | sgolayfilt | sos2cell |  |