
| Signal Processing Toolbox |   |
Elliptic analog lowpass filter prototype.
Syntax
[z,p,k] = ellipap(n,Rp,Rs)
Description
[z,p,k] = ellipap(n,Rp,Rs)
returns the zeros, poles, and gain of an order n elliptic analog lowpass filter prototype, with Rp dB of ripple in the passband, and a stopband Rs dB down from the peak value in the passband. The zeros and poles are returned in length n column vectors z and p and the gain in scalar k. If n is odd, z is length n - 1. The transfer function is
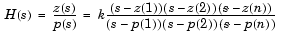
Elliptic filters offer steeper rolloff characteristics than Butterworth and Chebyshev filters, but they are equiripple in both the passband and the stopband. Of the four classical filter types, elliptic filters usually meet a given set of filter performance specifications with the lowest filter order.
ellip sets the cutoff frequency 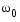 of the elliptic filter to 1 for a normalized result. The cutoff frequency is the frequency at which the passband ends and the filter has a magnitude response of 10-Rp/20.
of the elliptic filter to 1 for a normalized result. The cutoff frequency is the frequency at which the passband ends and the filter has a magnitude response of 10-Rp/20.
Algorithm
ellipap uses the algorithm outlined in [1]. It employs the M-file ellipk to calculate the complete elliptic integral of the first kind and the M-file ellipj to calculate Jacobi elliptic functions.
See Also
|
Bessel analog lowpass filter prototype. |
|
Butterworth analog lowpass filter prototype. |
|
Chebyshev type I analog lowpass filter prototype. |
|
Chebyshev type II analog lowpass filter prototype. |
|
Elliptic (Cauer) filter design. |
References
[1] Parks, T.W., and C.S. Burrus. Digital Filter Design. New York: John Wiley & Sons, 1987. Chapter 7.
 | ellip | ellipord |  |