| Target Language Compiler |
  |
Simulink External Mode and GRT
Objective: Become familiar with GRT, Simulink External Mode, and data logging. Before you begin, be sure to switch into an empty work directory.
Running External Mode in Simulink
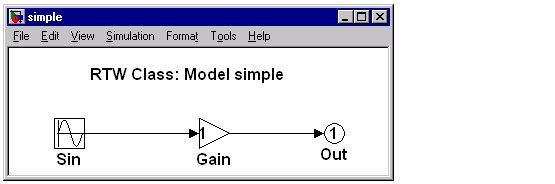
- Create the model
simple.mdl consisting of
- sine wave source block
- unity gain block
- outport
It should appear as the following.
- Set the following dialog options (Tools -> Real-Time Workshop -> Options)
- Solver page
fixed-step, discrete, step-size = 0.01 seconds, Stop time = 1000.0
- Workspace I/O
save Time as tout, save Output as yout, limit to last 1,000 pts., decimation = 1 (e.g., no decimation)
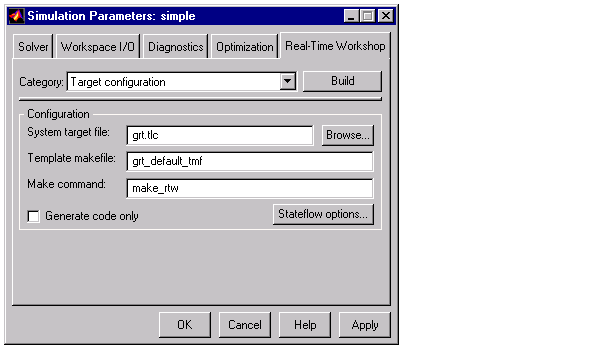
- Real-Time Workshop page
System target file: grt.tlc
Template makefile: grt_default_tmf (optionally: grt_watc.tmf, etc.)
Make command: make_rtw
Retain .rtw file
- Save
simple.mdl (File -> Save As)
Observe the dialog box entries in the following figure.
- Open External Mode Control Panel from the Tools menu.
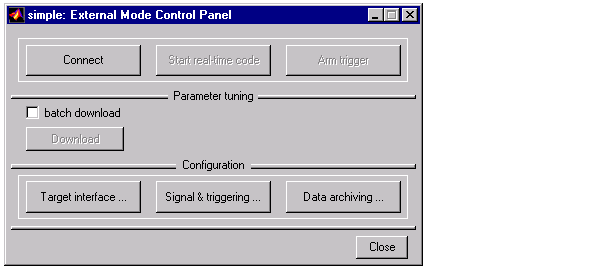
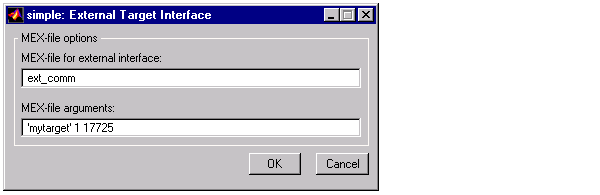
- Open the Target interface ... dialog and specify the MEX-file for external interface. For MEX-File arguments, the figure below options for the node name, verbosity = 1, and a port address that is selected as 17725. Defaults for MEX-file options would be your local host name and port 17725. Therefore, in this particular example, they could have been omitted. For targets where the target has a separate network ID, appropriate entries would be required.
- From the Real-Time Workshop page, go to the Options... dialog to select External mode check box. Click Build to generate the code and create the executable for non-real-time execution. Note that in order for this exercise to work, you must run the model for enough time steps so that you have enough time to change parameters before the model completes and ends. This explains the high value of stop time (1000.0 seconds) chosen earlier. You can also specify the running time when you execute the code.
- Open a DOS prompt window (i.e., a virtual DOS machine) and run the non-real-time executable. (Type
simple at the DOS command prompt.)
There are some options available for you to choose the running type. (Type
simple -tf for details.)
-tf 20 Sets final time to 20 seconds, inf runs forever.-port 300 Sets port to 300.-w Waits for start message from host.
- While the stand-alone simulation is running, start Simulink external mode.
- Select External from the Simulation menu.
- Go to External Mode Control Panel and click Connect to start.
- Immediately open the Gain block and change its value.
Once the execution is completed, it should create an output file, simple.mat.
- To load the generated MAT-file into MATLAB and plot the results, use
load simple
whos
plot(rt_tout, rt_yout)
 | Derivatives Function | | Advanced External Mode Exercise |  |





