

| Real-Time Workshop User's Guide |   |
Run-Time Structure
The real-time program executes on the VxWorks target while Simulink and StethoScope execute on the same or different host workstations. Both Simulink and StethoScope require tasks on the VxWorks target to handle communication.
This diagram illustrates the structure of a VxWorks application using Simulink external mode and StethoScope.
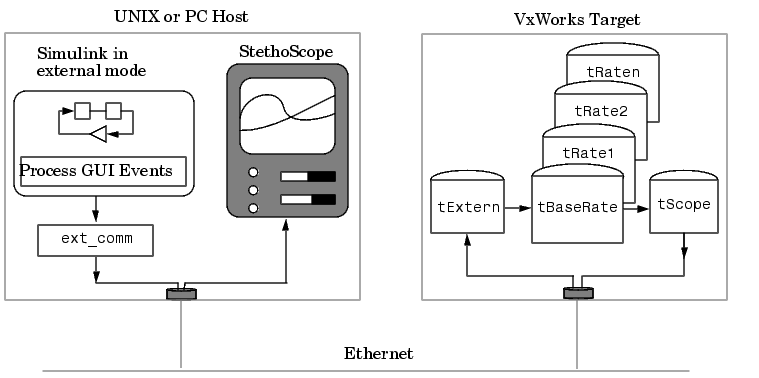
Figure 12-2: The Run-Time Structure
The program creates VxWorks tasks to run on the real-time system: one communicates with Simulink, the others execute the model. StethoScope creates its own tasks to collect data.
Host Processes
There are two processes running on the host side that communicate with the real-time program:
VxWorks Tasks
You can run the real-time program in either singletasking or multitasking mode. The code for both modes is located in
matlabroot/rtw/c/tornado/rt_main.c
The Real-Time Workshop compiles and links rt_main.c with the model code during the build process.
Singletasking. By default, the model is run as one task, tSingleRate. This may actually provide the best performance (highest base sample rate) depending on the model.
The tSingleRate task runs at the base rate of the model and executes all necessary code for the slower sample rates. Execution of the tSingleRate task is normally blocked by a call to the VxWorks semTake routine. When a clock interrupt occurs, the interrupt service routine calls the semGive routine, which causes the semTake call to return. Once enabled, the tSingleRate task executes the model code for one time step. The loop then waits at the top by again calling semTake. For more information about the semTake and semGive routines, refer to the VxWorks Reference Manual. By default, it runs at a relatively high priority (30), which allows it to execute without interruption from background system activity.
Multitasking. Optionally, the model can run as multiple tasks, one for each sample rate in the model:
tBaseRate -- This task executes the components of the model code run at the base (highest) sample rate. By default, it runs at a relatively high priority (30), which allows it to execute without interruption from background system activity. tRaten -- The program also spawns a separate task for each additional sample rate in the system. These additional tasks are named tRate1, tRate2, ..., tRaten, where n is slowest sample rate in the system. The priority of each additional task is one lower than its predecessor (tRate1 has a lower priority than tBaseRate).Supporting Tasks.. If you select external mode and/or StethoScope during the build process, these tasks will also be created:
t Extern -- This task implements the server side of a socket stream connection that accepts data transferred from Simulink to the real-time program. In this implementation, tExtern waits for a message to arrive from Simulink. When a message arrives, tExtern retrieves it and modifies the specified parameters accordingly.tExtern runs at a lower priority than tRaten, the lowest priority model task. The source code for tExtern is located in matlabroot/rtw/c/src/ext_svr.c.
tScopeDaemon and tScopeLink -- StethoScope provides its own VxWorks tasks to enable real-time data collection and display. In singletasking mode, tSingleRate collects signals; in multitasking mode, tBaseRate collects them. Both perform the collection on every base time step. The StethoScope tasks then send the data to the host for display when there is idle time, that is, when the model is waiting for the next time step to occur. rt_main.c starts these tasks if they are not already running. | Parameter Tuning and Monitoring | Implementation Overview |  |