| Partial Differential Equations Toolbox |   |
pdemesh(p,e,t) pdemesh(p,e,t,u) h=pdemesh(p,e,t) h=pdemesh(p,e,t,u)
Description
pdemesh(p,e,t)
plots the mesh specified by the mesh data p, e, and t.
h=pdemesh(p,e,t)
additionally returns handles to the plotted axes objects.
pdemesh(p,e,t,u)
plots PDE node or triangle data u using a mesh plot. If u is a column vector, node data is assumed. If u is a row vector, triangle data is assumed. This command plots substantially faster than the pdesurf command.
The geometry of the PDE problem is given by the mesh data p, e, and t. Details on the mesh data representation can be found in the entry on initmesh.
This command is just shorthand for the calls
» pdeplot(p,e,t) » pdeplot(p,e,t,'zdata',u)If you want to have more control over your mesh plot, use
pdeplot instead of pdemesh.
Examples
Plot the mesh for the geometry of the L-shaped membrane.
» [p,e,t]=initmesh('lshapeg');
» [p,e,t]=refinemesh('lshapeg',p,e,t);
» pdemesh(p,e,t)
Now solve Poisson's equation -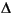 u = 1 over the geometry defined by the L-shaped membrane. Use Dirichlet boundary conditions u = 0 on
u = 1 over the geometry defined by the L-shaped membrane. Use Dirichlet boundary conditions u = 0 on 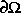 , and plot the result.
, and plot the result.
» u=assempde('lshapeb',p,e,t,1,0,1);
» pdemesh(p,e,t,u)
See Also
pdeplot, pdecont, pdesurf
 | pdemdlcv | pdenonlin |  |