| Motorola DSP Developer's Kit |   |
C = mot###_conv( A,B )
Description
This function convolves vectors A and B, where both A and B are complex vectors
Input/Output
Input: Complex vector A (Ar is the real part, and Ai is the imaginary part), and complex vector B (Br is the real part, and Bi is the imaginary part)
Output: Complex vector C (Cr is the real part, and Ci is the imaginary part)
Algorithm
LengthC = LengthB + LengthA - 1
for ( i = 1; i <= LengthC; i ++ ) {
if ( i <= LengthA ) {
for ( j = 1; j <= i; j ++ ) {
Cr[i] += Ar[j] * Br[i - j + 1] - Ai[j] * Bi[i - j + 1];
Ci[i] += Ai[j] * Br[i - j + 1] + Ar[j] * Bi[i - j + 1];
}
}
else {
for ( j = i - LengthA; j <= LengthA - 1; j ++ ) {
Cr[i] += Ar[j + 1] * Br[i - j] - Ai[j + 1] * Bi[i - j];
Ci[i] += Ai[j + 1] * Br[i - j] + Ar[j + 1] * Bi[i - j];
}
}
}
Memory & Register
M{0,1,2,3,4,6,7} = $ffffffStatus Register
The assembly function conv-c.asm does not set any status registers/bits during function execution.
Data Size Limit
The maximum length of vector A and B can't be larger than 1/4 of the continuous available data memory size.
Data Range Limit
The input data vector range is [-1.0, +1.0].
Precision
In the case of DSP563, precision is the full 23 bits.
In the case of DSP566, precision is the full 15 bits.
Performance Limit
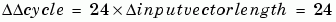
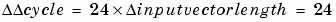
 | conv-r.asm | decimate-fir-r.asm |  |