

| Using the C Math Library |   |
Error Messages
This section lists a subset of the error messages issued by the library. By default, programs written using the library always exit after an error has occurred. For information about handling errors so that you can continue processing after an error occurred, see Error Handling Overview in Chapter 8.
An input argument that must be either 1-by-N or M-by-1, i.e., either a row or column vector, was an M-by-N matrix where neither M nor N is equal to 1. To correct this, check the documentation for the function that produced the error and fix the incorrect argument.
Division by zero is not allowed
The MATLAB C Math Library detected an attempt to divide by zero. This error only occurs on non-IEEE machines (notably DEC VAX machines), which cannot represent infinity. Division by zero on IEEE machines results in a warning rather than an error.
Empty matrix is not a valid argument
Some functions, such as mlfSize, accept empty matrices as input arguments. Others, such as mlfEig, do not. You will see this error message if you call a function that does not accept NULL matrices with a NULL matrix.
A computation generated a floating-point number larger than the maximum number representable on the current machine. Check your inputs to see if any are near zero (if dividing) or infinity (if adding or multiplying).
Initial condition vector is not the right length
This error is issued only by the mlfFilter function. The length of the initial condition vector must be equal to the maximum of the products of the dimensions of the input filter arguments. Let the input filter arguments be given by matrices B and A, with dimensions bM-by-bN and aM-by-aN respectively. Then the length of the initial condition vector must be equal to the maximum of bM * bN and aM * aN.
Inner matrix dimensions must agree
Given two matrices, A and B, with dimensions aN-by-aM and bN-by-bM, the inner dimensions referred to by this error message are aM and bN. These dimensions must be equal. This error occurs, for example, in matrix multiplication; an N-by-2 matrix can only be multiplied by a scalar or a 2-by-M matrix. Any attempt to multiply it by a matrix with other than two rows will cause this error.
Taking the log of zero produces negative infinity. On non-IEEE floating point machines, this is an error, because such machines cannot represent infinity.
This error occurs when a function expects two or more matrices to be identical in size and they are not. For example, the inputs to mlfPlus, which computes the sums of the elements of two matrices, must be of equal size. To correct this error, make sure the required input matrices are the same size.
Matrix is singular to working precision
A matrix is singular if two or more of its columns are not linearly independent. Singular matrices cannot be inverted. This error message indicates that two or more columns of the matrix are linearly dependent to within the floating-point precision of the machine.
Matrix must be positive definite
A matrix is positive definite if and only if x'Ax > 0 for all nonzero vectors x. This error message indicates that the input matrix was not positive definite.
A function expected a square matrix. For example, mlfQz, which computes generalized eigenvalues, expects both of its arguments to be square matrices. An M-by-N matrix is square if and only if M and N are equal.
Maximum variable size allowed by the program is exceeded
This error occurs when an integer variable is larger than the maximum representable integer on the machine. This error occurs because all matrices contain double precision values, yet some routines require integer values; and the maximum representable double precision value is much larger than the maximum representable integer. Correct this error by checking the documentation for the function that produced it. Make sure that all input arguments that are treated as integers are less than or equal to the maximum legal value for an integer.
IEEE NaN (Not-A-Number) or Inf (Infinity) was passed to a function that cannot handle those values, or resulted unexpectedly from computations internal to a function.
A function expected more input arguments than it was passed. For example, most functions will issue this error if they receive zero arguments. The MATLAB C Math Library should never issue this error. Please notify The MathWorks if you see this error message.
A function expected more output arguments than were passed to it. Functions in the MATLAB C Math Library will issue this error if any required output arguments are NULL. If you see this error under any other conditions, please notify The MathWorks.
A singularity indicates an input for which the output is undefined. ATAN (arc tangent) has singularities on the complex plane, particularly at z = 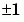 .
.
A singularity indicates an input for which the output is undefined. TAN (tangent function) has singularities at odd multiples of 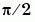 .
.
This error occurs when the input to a function is poorly conditioned or otherwise beyond the capabilities of our iterative algorithms to solve.
String argument is an unknown option
A function received a string matrix (i.e., a matrix with the string property set to true) when it was not expecting one. For example, most of the matrix creation functions, for example, mlfEye and mlfZeros, issue this error if any of their arguments are string matrices.
The only matrix norms available are 1, 2, inf and fro
The function mlfNorm has an optional second argument. This argument must be either the scalars 1 or 2 or the strings inf or fro. inf indicates the infinity norm and fro the F-norm. This error occurs when the second argument to mlfNorm is any value other than one of these four values.
This error occurs when a function has more input arguments passed to it than it expects. The MATLAB C Math Library should never issue this error, as this condition should be detected by the C compiler. Please notify The MathWorks if you see this error.
This error occurs when a function has more output arguments passed to it than it expects. The MATLAB C Math Library should never issue this error, as this condition should be detected by the C compiler. Please notify The MathWorks if you see this error.
Variable must contain a string
An argument to a function should have been a string matrix (i.e., a matrix with the string property set to true), but was not.
Zero can't be raised to a negative power
On machines with non-IEEE floating point format, the library does not permit you to raise zero to any negative power, as this would result in a division by zero, since x^(-y) == 1/(x^y) and 0^n == 0. Non-IEEE machines cannot represent infinity, so division by zero is an error on those machines (mostly DEC VAXes).
 | Errors and Warnings | Warning Messages |  |