| Instrument Control Toolbox |   |
Example: Reading Binary Data
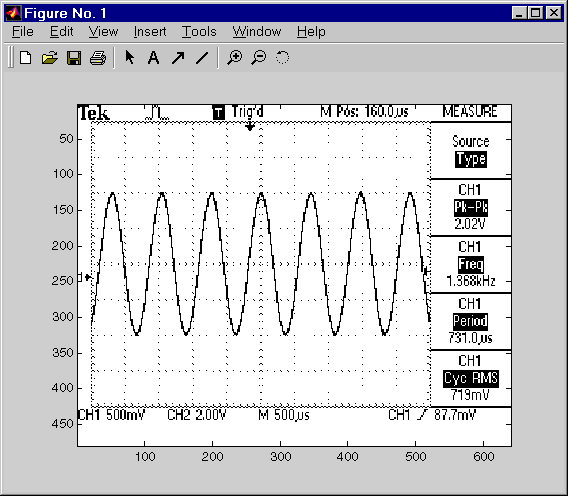
This example illustrates how you can download the TDS 210 oscilloscope screen display to MATLAB. The screen display data is transferred to MATLAB and saved to disk using the Windows bitmap format. This data provides a permanent record of your work, and is an easy way to document important signal and scope parameters.
1. Create an instrument object - Create the GPIB object g associated with a National Instruments GPIB controller with board index 0, and an instrument with primary address 1.
g = gpib('ni',0,1);
2. Configure property values - Configure the input buffer to accept a reasonably large number of bytes, and configure the timeout value to two minutes to account for slow data transfer.
g.InputBufferSize = 50000; g.Timeout = 120;
3. Connect to the instrument - Connect g to the oscilloscope.
fopen(g)
4. Write and read data - Configure the scope to transfer the screen display as a bitmap.
fprintf(g,'HARDCOPY:PORT GPIB') fprintf(g,'HARDCOPY:FORMAT BMP') fprintf(g,'HARDCOPY START')
Asynchronously transfer the data from the instrument to the input buffer.
readasync(g)
Wait until the read operation completes, and then transfer the data to the MATLAB workspace as unsigned 8-bit integers.
g.TransferStatus ans = idle out = fread(g,g.BytesAvailable,'uint8');
5. Disconnect and clean up - When you no longer need g, you should disconnect it from the instrument, and remove it from memory and from the MATLAB workspace.
fclose(g) delete(g) clear g
Viewing the Bitmap Data
To view the bitmap data, you should follow these steps:
imread function.
imagesc function.
Note that MATLAB's file I/O versions of the fopen, fwrite, and fclose functions are used.
fid = fopen('test1.bmp','w');
fwrite(fid,out,'uint8');
fclose(fid)
a = imread('test1.bmp','bmp');
imagesc(fliplr(a'))
Since the scope returns the screen display data using only two colors, an appropriate colormap is selected.
mymap = [0 0 0; 1 1 1]; colormap(mymap)
The resulting bitmap image is shown below.
 | Example: Writing and Reading Text Data | Example: Parsing Input Data Using strread |  |