

| Image Processing Toolbox |   |
Binary Images
In a binary image, each pixel assumes one of only two discrete values. Essentially, these two values correspond to on and off. A binary image is stored as a two-dimensional matrix of 0's (off pixels) and 1's (on pixels).
A binary image can be considered a special kind of intensity image, containing only black and white. Other interpretations are possible, however; you can also think of a binary image as an indexed image with only two colors.
A binary image can be stored in an array of class double or uint8. (The toolbox does not support binary images of class uint16.) An array of class uint8 is generally preferable to an array of class double, because a uint8 array uses far less memory. In the Image Processing Toolbox, any function that returns a binary image returns it as a uint8 logical array. The toolbox uses a logical flag to indicate the data range of a uint8 logical array: if the logical flag is "on" the data range is [0,1]; if the logical flag is off, the toolbox assumes the data range is [0,255].)
The figure below depicts a binary image.
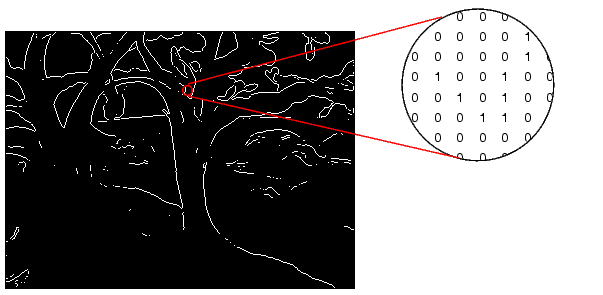
Figure 2-3: Pixels in A Binary Image Have Two Possible Values: 0 or 1
 | Intensity Images | RGB Images |  |