

| Image Processing Toolbox |   |
Syntax
h = fspecial(type) h = fspecial(type,parameters)
Description
h = fspecial(type) creates a two-dimensional filter h of the specified type. (fspecial returns h as a computational molecule, which is the appropriate form to use with filter2.) type is a string having one of these values:
'gaussian' for a Gaussian lowpass filter'sobel' for a Sobel horizontal edge-emphasizing filter'prewitt' for a Prewitt horizontal edge-emphasizing filter'laplacian' for a filter approximating the two-dimensional Laplacian operator'log' for a Laplacian of Gaussian filter'average' for an averaging filter'unsharp' for an unsharp contrast enhancement filterh = fspecial(type,parameters) accepts a filter type plus additional modifying parameters particular to the type of filter chosen. If you omit these arguments, fspecial uses default values for the parameters.
The following list shows the syntax for each filter type. Where applicable, additional parameters are also shown.
h = fspecial('gaussian',n,sigma) returns a rotationally symmetric Gaussian lowpass filter with standard deviation sigma (in pixels). n is a 1-by-2 vector specifying the number of rows and columns in h. (n can also be a scalar, in which case h is n-by-n.) If you do not specify the parameters, fspecial uses the default values of [3 3] for n and 0.5 for sigma.h = fspecial('sobel') returns this 3-by-3 horizontal edge-finding and y-derivative approximation filter: [ 1 2 1 0 0 0 -1 -2 -1 ]
To find vertical edges, or for x-derivatives, use h'.
h = fspecial('prewitt') returns this 3-by-3 horizontal edge-finding and y-derivative approximation filter: [ 1 1 1 0 0 0 -1 -1 -1 ]
To find vertical edges, or for x-derivatives, use h'.
h = fspecial('laplacian',alpha) returns a 3-by-3 filter approximating the two-dimensional Laplacian operator. The parameter alpha controls the shape of the Laplacian and must be in the range 0 to 1.0. fspecial uses the default value of 0.2 if you do not specify alpha.h = fspecial('log',n,sigma) returns a rotationally symmetric Laplacian of Gaussian filter with standard deviation sigma (in pixels). n is a 1-by-2 vector specifying the number of rows and columns in h. (n can also be a scalar, in which case h is n-by-n.) If you do not specify the parameters, fspecial uses the default values of [5 5] for n and 0.5 for sigma.h = fspecial('average',n) returns an averaging filter. n is a 1-by-2 vector specifying the number of rows and columns in h. (n can also be a scalar, in which case h is n-by-n.) If you do not specify n, fspecial uses the default value of [3 3]. h = fspecial('unsharp',alpha) returns a 3-by-3 unsharp contrast enhancement filter. fspecial creates the unsharp filter from the negative of the Laplacian filter with parameter alpha. alpha controls the shape of the Laplacian and must be in the range 0 to 1.0. fspecial uses the default value of 0.2 if you do not specify alpha.Example
I = imread('saturn.tif');
h = fspecial('unsharp',0.5);
I2 = filter2(h,I)/255;
imshow(I)
figure, imshow(I2)
Algorithms
fspecial creates Gaussian filters using
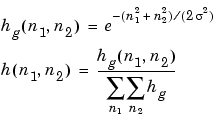
fspecial creates Laplacian filters using
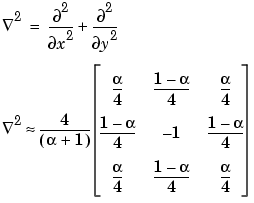
fspecial creates Laplacian of Gaussian (LoG) filters using
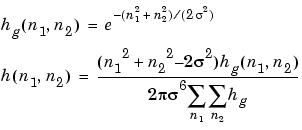
fspecial creates averaging filters using
ones(n(1),n(2))/(n(1)*n(2))
fspecial creates unsharp filters using
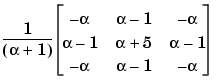
See Also
conv2, edge, filter2, fsamp2, fwind1, fwind2
del2 in the MATLAB Function Reference
 | fsamp2 | ftrans2 |  |