| Image Processing Toolbox |   |
Lookup Table Operations
Certain binary image operations can be implemented most easily through lookup tables. A lookup table is a column vector in which each element represents the value to return for one possible combination of pixels in a neighborhood.
You can use the makelut function to create lookup tables for various operations. makelut creates lookup tables for 2-by-2 and 3-by-3 neighborhoods. This figure illustrates these types of neighborhoods. Each neighborhood pixel is indicated by an x, and the center pixel is the one with a circle.
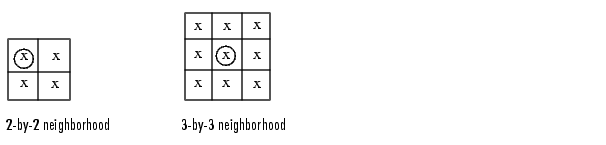
For a 2-by-2 neighborhood, there are 16 possible permutations of the pixels in the neighborhood. Therefore, the lookup table for this operation is a 16-element vector. For a 3-by-3 neighborhood, there are 512 permutations, so the lookup table is a 512-element vector.
Once you create a lookup table, you can use it to perform the desired operation by using the applylut function.
The example below illustrates using lookup-table operations to modify an image containing text. You begin by writing a function that returns 1 if three or more pixels in the 3-by-3 neighborhood are 1, and 0 otherwise. You then call makelut, passing in this function as the first argument, and using the second argument to specify a 3-by-3 lookup table.
f = inline('sum(x(:)) >= 3');
lut = makelut(f,3);
lut is returned as a 512-element vector of 1's and 0's. Each value is the output from the function for one of the 512 possible permutations.
You then perform the operation using applylut.
BW1 = imread('text.tif');
BW2 = applylut(BW1,lut);
imshow(BW1)
figure, imshow(BW2)
Figure 9-8: Text.tif Before and After Applying a Lookup Table Operation
For information about how applylut maps pixel combinations in the image to entries in the lookup table, see the reference page for applylut.
 | Euler Number | Region-Based Processing |  |