| Communications Blockset |
  |
M-PAM Modulator Passband
Modulate using M-ary pulse amplitude modulation
Library
AM, in Digital Passband sublibrary of Modulation
Description
The M-PAM Modulator Passband block modulates using M-ary pulse amplitude modulation. The output is a passband representation of the modulated signal. The M-ary number parameter, M, is the number of points in the signal constellation. It must be an even integer.
This block uses the baseband equivalent block, M-PAM Modulator Baseband, for internal computations and converts the resulting baseband signal to a passband representation. The following parameters in this block are the same as those of the baseband equivalent block:
- M-ary number
- Input type
- Constellation ordering
- Normalization method
- Minimum distance
- Average power
- Peak power
The input must be sample-based. If the Input type parameter is Bit, then the input must be a vector of length log2(M). If the Input type parameter is Integer, then the input must be a scalar.
Parameters Specific to Passband Simulation
Passband simulation uses a carrier signal. The Carrier frequency and Carrier initial phase parameters specify the frequency and initial phase, respectively, of the carrier signal. The Symbol period parameter must equal the sample time of the input signal, while the Output sample time parameter determines the sample time of the output signal.
This block uses a baseband representation of the modulated signal as an intermediate result during internal computations. The Baseband samples per symbol parameter indicates how many baseband samples correspond to each integer or binary word in the input, before the block converts them to a passband output.
The timing-related parameters must satisfy these relationships:
- Symbol period > (Carrier frequency)-1
- Output sample time < [2*Carrier frequency + 2/(Symbol period)]-1
- Symbol period = K*Output sample time*Baseband samples per symbol for some integer K
Furthermore, Carrier frequency is typically much larger than the highest frequency of the unmodulated signal.
Dialog Box
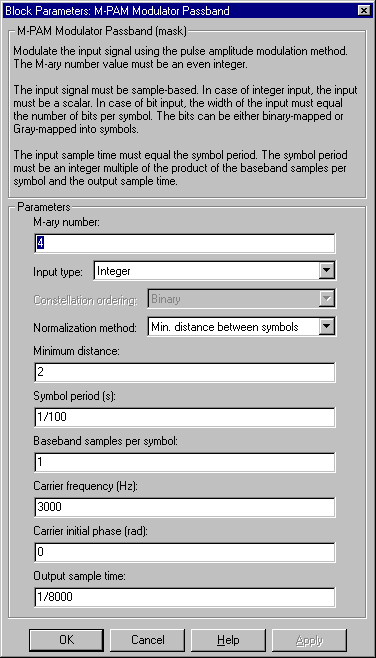
- M-ary number
- The number of points in the signal constellation. It must be an even integer.
- Input type
- Indicates whether the input consists of integers or groups of bits. If this parameter is set to Bit, then the M-ary number parameter must be 2K for some positive integer K.
- Constellation ordering
- Determines how the block maps each group of input bits to a corresponding integer. This field is active only when Input type is set to Bit.
- Normalization method
- Determines how the block scales the signal constellation. Choices are Min. distance between symbols, Average Power, and Peak Power.
- Minimum distance
- The distance between two nearest constellation points. This field appears only when Normalization method is set to Min. distance between symbols.
- Average power (watts)
- The average power of the symbols in the constellation. This field appears only when Normalization method is set to Average Power.
- Peak power (watts)
- The maximum power of the symbols in the constellation. This field appears only when Normalization method is set to Peak Power.
- Symbol period (s)
- The symbol period, which must equal the sample time of the input.
- Baseband samples per symbol
- The number of baseband samples that correspond to each integer or binary word in the input, before the block converts them to a passband output.
- Carrier frequency (Hz)
- The frequency of the carrier.
- Carrier initial phase (rad)
- The initial phase of the carrier in radians.
- Output sample time
- The sample time of the output signal.
Pair Block
M-PAM Demodulator Passband
See Also
M-PAM Modulator Baseband
 | M-PAM Modulator Baseband | | M-PSK Demodulator Baseband |  |






