| MATLAB Function Reference |   |
Syntax
FX = gradient(F) [FX,FY] = gradient(F) [Fx,Fy,Fz,...] = gradient(F) [...] = gradient(F,h) [...] = gradient(F,h1,h2,...)
Definition
The gradient of a function of two variables, F(x,y), is defined as:
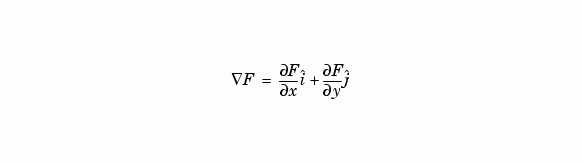
and can be thought of as a collection of vectors pointing in the direction of increasing values of 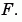 In MATLAB, numerical gradients (differences) can be computed for functions with any number of variables. For a function of N variables, F(x,y,z,...),
In MATLAB, numerical gradients (differences) can be computed for functions with any number of variables. For a function of N variables, F(x,y,z,...),

Description
FX = gradient(F)
where F is a vector returns the one-dimensional numerical gradient of F. FX corresponds to 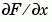 , the differences in the x direction.
, the differences in the x direction.
[FX,FY] = gradient(F)
where F is a matrix returns the x and y components of the two-dimensional numerical gradient. FX corresponds to 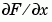 , the differences in the
, the differences in the x (column) direction. FY corresponds to 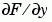 , the differences in the y (row) direction. The spacing between points in each direction is assumed to be one.
, the differences in the y (row) direction. The spacing between points in each direction is assumed to be one.
[FX,FY,FZ,...] = gradient(F)
where F has N dimensions returns the N components of the gradient of F. There are two ways to control the spacing between values in F:
h, specifies the spacing between points in every direction.N spacing values (h1,h2,...) specifies the spacing for each dimension of F. Scalar spacing parameters specify a constant spacing for each dimension. Vector parameters specify the coordinates of the values along corresponding dimensions of F. In this case, the length of the vector must match the size of the corresponding dimension.[...] = gradient(F,h)
where h is a scalar uses h as the spacing between points in each direction.
[...] = gradient(F,h1,h2,...)
with N spacing parameters specifies the spacing for each dimension of F.
Examples
v = -2:0.2:2; [x,y] = meshgrid(v); z = x .* exp(-x.^2 - y.^2); [px,py] = gradient(z,.2,.2); contour(v,v,z), hold on, quiver(px,py), hold off
F(:,:,1) = magic(3); F(:,:,2) = pascal(3);gradient(F)takesdx=dy=dz=1.[PX,PY,PZ] = gradient(F,0.2,0.1,0.2)takesdx = 0.2,dy = 0.1, anddz = 0.2.
See Also
 | gplot | graymon |  |