

| Programming and Data Types |   |
Accessing Data in Structure Arrays
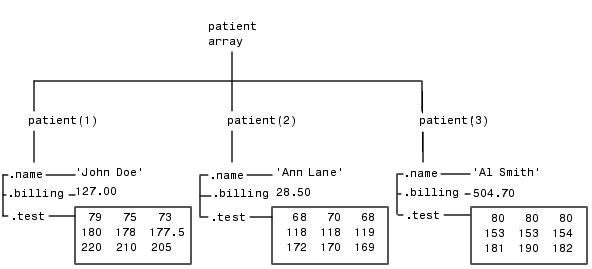
Using structure array indexing, you can access the value of any field or field element in a structure array. Likewise, you can assign a value to any field or field element. For the examples in this section, consider this structure array.
You can access subarrays by appending standard subscripts to a structure array name. For example, the line below results in a 1-by-2 structure array.
mypatients = patient(1:2)
1x2 struct array with fields:
name
billing
test
The first structure in the mypatients array is the same as the first structure in the patient array.
mypatients(1)
ans =
name: 'John Doe'
billing: 127
test: [3x3 double]
To access a field of a particular structure, include a period (.) after the structure name followed by the field name.
str = patient(2).name str = Ann Lane
To access elements within fields, append the appropriate indexing mechanism to the field name. That is, if the field contains an array, use array subscripting; if the field contains a cell array, use cell array subscripting, and so on.
test2b = patient(3).test(2,2) test2b = 153
Use the same notations to assign values to structure fields, for example,
patient(3).test(2,2) = 7;
You can extract field values for multiple structures at a time. For example, the line below creates a 1-by-3 vector containing all of the billing fields.
bills = [patient.billing] bills = 127.0000 28.5000 504.7000
Similarly, you can create a cell array containing the test data for the first two structures.
tests = {patient(1:2).test}
tests =
[3x3 double] [3x3 double]
Accessing Field Values Using setfield and getfield
Direct indexing is usually the most efficient way to assign or retrieve field values. If, however, you only know the field name as a string - for example, if you have used the fieldnames function to obtain the field name within an M-file - you can use the setfield and getfield functions to do the same thing.
getfield obtains a value or values from a field or field element
f = getfield(array,{array_index},'field',{field_index})
where the field_index is optional, and array_index is optional for a 1-by-1 structure array. The function syntax corresponds to
f=array(array_index).field(field_index);
For example, to access the name field in the second structure of the patient array, use:
str = getfield(patient,{2},'name');
Similarly, setfield lets you assign values to fields using the syntax
f = setfield(array,{array_index},'field',{field_index},value)
 | Building Structure Arrays | Finding the size of Structure Arrays |  |