| External Interfaces/API |   |
Required Arguments to a MEX-File
The two components of the MEX-file may be separate or combined. In either case, the files must contain the #include "mex.h" header so that the entry point and interface routines are declared properly. The name of the gateway routine must always be mexFunction and must contain these parameters:
void mexFunction(
int nlhs, mxArray *plhs[],
int nrhs, const mxArray *prhs[])
{
/* more C code ... */
The parameters nlhs and nrhs contain the number of left- and right-hand arguments with which the MEX-file is invoked. In the syntax of the MATLAB language, functions have the general form
[a,b,c,...] = fun(d,e,f,...)
where the ellipsis (...) denotes additional terms of the same format. The a,b,c,... are left-hand arguments and the d,e,f,... are right-hand arguments.
The parameters plhs and prhs are vectors that contain pointers to the left- and right-hand arguments of the MEX-file. Note that both are declared as containing type mxArray *, which means that the variables pointed at are MATLAB arrays. prhs is a length nrhs array of pointers to the right-hand side inputs to the MEX-file, and plhs is a length nlhs array that will contain pointers to the left-hand side outputs that your function generates. For example, if you invoke a MEX-file from the MATLAB workspace with the command
x = fun(y,z);
the MATLAB interpreter calls mexFunction with the arguments
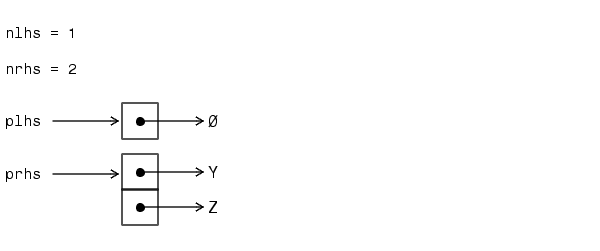
plhs is a 1-element C array where the single element is a null pointer. prhs is a 2-element C array where the first element is a pointer to an mxArray named Y and the second element is a pointer to an mxArray named Z.
The parameter plhs points at nothing because the output x is not created until the subroutine executes. It is the responsibility of the gateway routine to create an output array and to set a pointer to that array in plhs[0]. If plhs[0] is left unassigned, MATLAB prints a warning message stating that no output has been assigned.
Note
It is possible to return an output value even if nlhs = 0. This corresponds to returning the result in the ans variable.
|
 | Creating C Language MEX-Files | Examples of C MEX-Files |  |