| Getting Started |   |
Function Functions
A class of functions, called "function functions," works with nonlinear functions of a scalar variable. That is, one function works on another function. The function functions include:
MATLAB represents the nonlinear function by a function M-file. For example, here is a simplified version of the function humps from the matlab/demos directory.
function y = humps(x) y = 1./((x-.3).^2 + .01) + 1./((x-.9).^2 + .04) - 6;
Evaluate this function at a set of points in the interval 0 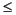 x
x 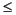 1 with
1 with
x = 0:.002:1; y = humps(x);
plot(x,y)
The graph shows that the function has a local minimum near x = 0.6. The function fminsearch finds the minimizer, the value of x where the function takes on this minimum. The first argument to fminsearch is a function handle to the function being minimized and the second argument is a rough guess at the location of the minimum.
p = fminsearch(@humps,.5)
p =
0.6370
To evaluate the function at the minimizer,
humps(p) ans = 11.2528
Numerical analysts use the terms quadrature and integration to distinguish between numerical approximation of definite integrals and numerical integration of ordinary differential equations. MATLAB's quadrature routines are quad and quadl. The statement
Q = quadl(@humps,0,1)
computes the area under the curve in the graph and produces
Q = 29.8583
Finally, the graph shows that the function is never zero on this interval. So, if you search for a zero with
z = fzero(@humps,.5)
you will find one outside of the interval
z = -0.1316
 | Function Handles | Demonstration Programs Included with MATLAB |  |