Wavelet analysis example from Matlab wavelet toolbox
Make plots for wavelet example from Matlab toolbox using electrical consumption time series leleccum (sampling rate 1/minute; tabulated over 2.7 days)
Contents
Load data
load leleccum;
s = leleccum(1:4096);
ls = length(s);
Plot signal
figure(1) subplot(3,1,1) plot(s,'k') v = axis; v(1:2) = [0 ls]; axis(v); ylabel('s')
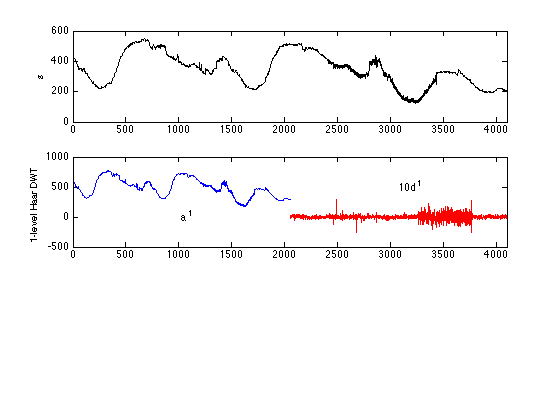
Plot level-1 Haar transform of s
[cA1,cD1] = dwt(s,'db1'); % Single-level Haar (db1) wavelet transform A1 = upcoef('a',cA1,'db1',1,ls); % Average time series D1 = upcoef('d',cD1,'db1',1,ls); % Detail time series subplot(3,1,2) plot(1:ls/2,cA1,'b',(ls/2+1):ls,10*cD1,'r') v = axis; v(1:2) = [0 ls]; axis(v); text(ls/4,0,'a^1') text(3*ls/4,500,'10d^1') ylabel('1-level Haar DWT')
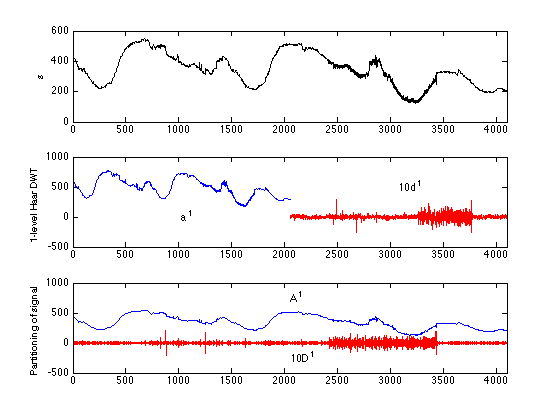
Plot partitioning of signal into average and detail components.
subplot(3,1,3) plot(1:ls,A1,'b',1:ls,10*D1,'r') v = axis; v(1:2) = [0 ls]; axis(v); text(ls/2,750,'A^1') text(ls/2,-250,'10D^1') ylabel('Partitioning of signal')
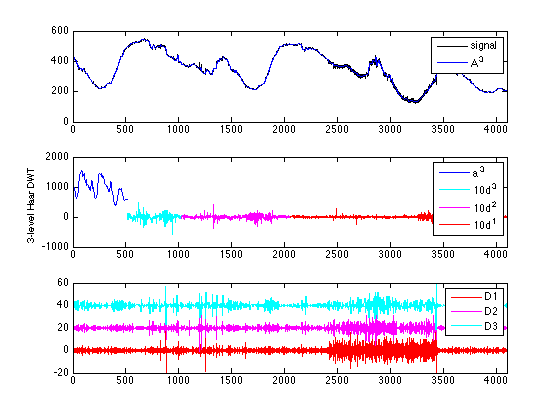
3-level Haar transform
figure(2) [C,L] = wavedec(s,3,'db1'); A3 = wrcoef('a',C,L,'db1',3); D1 = wrcoef('d',C,L,'db1',1); D2 = wrcoef('d',C,L,'db1',2); D3 = wrcoef('d',C,L,'db1',3) ; % Plot signal and the 3rd level averaged signal subplot(3,1,1) plot(1:ls,s,'k',1:ls,A3,'b') v = axis; v(1:2) = [0 ls]; axis(v); legend('signal','A^3') % Plot level-3 Haar transform subplot(3,1,2) plot(1:ls/8,C(1:ls/8),'b',(ls/8+1):(ls/4),10*C((ls/8+1):(ls/4)),'c',... (ls/4+1):(ls/2),10*C((ls/4+1):(ls/2)),'m',... (ls/2+1):ls,10*C((ls/2+1):ls),'r') v = axis; v(1:2) = [0 ls]; axis(v); ylabel('3-level Haar DWT') legend('a^3','10d^3','10d^2','10d^1') % Plot the three detail components of signal subplot(3,1,3) yoff = 20; plot(1:ls,D1,'r',1:ls,D2+yoff,'m',1:ls,D3+2*yoff,'c') v = axis; v(1:2) = [0 ls]; axis(v); ; axis([0,ls,-20,60]) legend('D1','D2','D3')
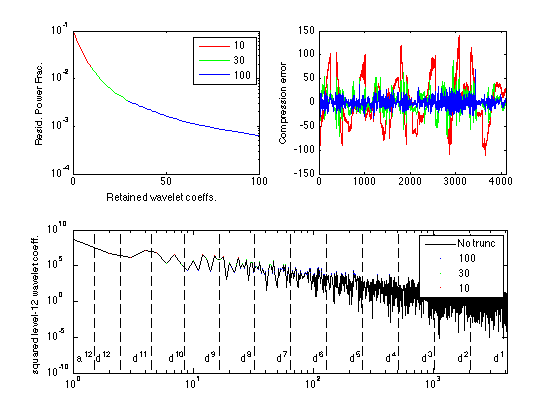
Signal compression
p = log2(ls); s2 = leleccum(1:ls); % Calculate complete p-level Haar transform [C,L] = wavedec(s2,p,'db1'); % Plot the largest nkeep wavelet coefficients, for various % choices nkeep figure(3) subplot(2,2,1) Csq = C.^2; [mCsqsort,Isort] = sort(-Csq); % Tricky way to sort wavelet coeffs from % largest to smallest in magnitude. cumpow = cumsum(mCsqsort)/sum(mCsqsort); % Cum frac of Wavelet power nkeep = [10 30 100]; semilogy(1:nkeep(1),1-cumpow(1:nkeep(1)),'r',... nkeep(1):nkeep(2),1-cumpow(nkeep(1):nkeep(2)),'g',... nkeep(2):nkeep(3),1-cumpow(nkeep(2):nkeep(3)),'b'); xlabel('Retained wavelet coeffs.') ylabel('Resid. Power Frac.') legend(int2str(nkeep(1)),int2str(nkeep(2)),int2str(nkeep(3))) % Reconstruct signal if other wavelet coeffs are zeroed out and % plot 'compression error' in the signal that this induces. subplot(2,2,2) col = 'rgb'; % Vector of plotting colors for ik = 1:length(nkeep) jsort = Isort(1:nkeep(ik)); C2 = C - C; % Zero wavelet coeffs of compressed signal C2(jsort) = C(jsort); % ...except for the nkeep(ik) largest. sc = waverec(C2,L,'db1'); % Reconstruction after compression plot(1:ls, sc-s, col(ik)) if (ik==1) v = axis; v(1:2) = [0 ls]; axis(v); ylabel('Compression error') hold on end end % legend(int2str(nkeep(1)),int2str(nkeep(2)),int2str(nkeep(3))) hold off subplot(2,1,2) loglog(1:ls,Csq,'k',Isort(1:nkeep(3)),-mCsqsort(1:nkeep(3)),'b.',... Isort(1:nkeep(2)),-mCsqsort(1:nkeep(2)),'g.',... Isort(1:nkeep(1)),-mCsqsort(1:nkeep(1)),'r.') v = axis; v(1:2) = [0 ls]; axis(v); ylabel('squared level-12 wavelet coeff.') legend('No trunc',int2str(nkeep(3)),int2str(nkeep(2)),int2str(nkeep(1))) hold on ytxt = v(3)^0.9 * v(4)^0.1; text(1.1,ytxt,'a^{12}') for lev = 1:p plot([2^(p-lev)+0.5 2^(p-lev)+0.5],[v(3) v(4)],'k--') text(1.55*2^(p-lev),ytxt,['d^{' num2str(lev) '}']) end hold off